NRZ vs PAM4: Understanding the Key Differences
Advertisement
Both PAM4 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation with four levels) and NRZ (Non-Return-to-Zero) are digital modulation or signaling schemes used to transmit digital data over communication channels. Both are different modulation types and have distinct characteristics.
Let’s understand each of these modulation schemes before we explore the difference between NRZ and PAM4.
NRZ Encoding or Modulation
NRZ (Non-Return-to-Zero) encoding is a simple binary modulation technique widely used in digital communication to represent digital data. In NRZ, each bit is assigned a constant voltage level for the entire duration of the bit period.
A high voltage level typically represents one binary state (‘1’), while a low voltage level represents the other state (‘0’). NRZ encoding is straightforward to implement, making it a common choice for various communication systems.
However, one challenge with NRZ is its potential for a DC (direct current) component, which can affect signal integrity and may require additional measures for long-term transmission reliability.
Despite this limitation, NRZ remains popular in many applications due to its simplicity and ease of implementation.
Following are the types of NRZ encoding.
- Unipolar NRZ encoding
- Polar NRZ encoding
- Bipolar NRZ encoding
PAM4 Modulation
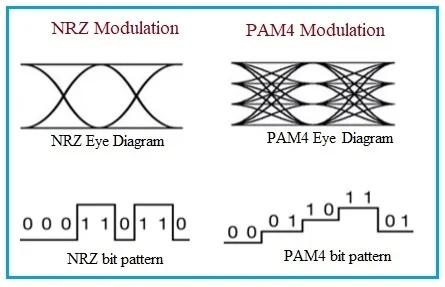
PAM4, or Pulse Amplitude Modulation with four levels, is a sophisticated digital modulation technique used in communication systems to transmit data efficiently over a communication channel. In PAM4, each symbol represents four different signal levels, allowing the transmission of two bits per symbol.
The four levels are typically represented as -3, -1, +1, and +3 (or 0, 1, 2, 3), and each combination of these levels corresponds to a specific pair of bits. This higher density of information per symbol enables PAM4 to achieve higher data rates and spectral efficiency compared to traditional binary modulation schemes.
PAM4 is particularly prevalent in applications demanding substantial data throughput, such as data center interconnects and optical fiber communication, where its capacity to transmit more bits per symbol contributes to increased bandwidth and improved overall system performance.
Difference between NRZ and PAM4 modulation
The following table compares NRZ vs PAM4 and mentions the difference between NRZ and PAM4 modulation types with respect to various parameters including number of levels, bit representation, spectral efficiency, complexity, noise sensitivity, applications, etc.
| Features | NRZ | PAM4 |
|---|---|---|
| Full form | Non-Return-to-Zero | Pulse Amplitude Modulation with four levels |
| Number of Levels | Two levels (0 and 1) | Four levels (-3, -1, +1, +3 or 0, 1, 2, 3) |
| Bit Representation | Each bit corresponds to one level | Each symbol represents two bits |
| Spectral efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Complexity | Lower, simple timing recovery due to binary nature | Higher, more complex timing recovery due to multiple levels |
| Power consumption | Generally have low power consumption | May have higher power consumption due to complexity |
| Noise sensitivity | Potentially less susceptible to noise, better signal integrity | More susceptible to noise |
| Eye diagram | Typically has wider and more open eye diagram | Eye diagram may be narrower and more challenging |
| Bit Error Rate (BER) | BER may be lower due to simple decoding | BER may be higher due to increased complexity |
| Transmission distance | Can achieve longer transmission distances | Transmission distance may be limited |
| Applications | Commonly used in various communications systems | Often used in high-speed communication systems, especially optical fiber communication for data centers and high-performance computing |
Conclusion
In summary, NRZ and PAM4 are different modulation schemes with varying levels, bit representations, spectral efficiency, complexity, noise sensitivity, and applications.
The choice between NRZ and PAM4 depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the communication system.
Advertisement
 RF
RF







