GDDR vs HBM: Key Differences in Graphics Memory
Advertisement
This article explores the differences between GDDR (Graphics Double Data Rate) and HBM (High Bandwidth Memory), two prominent memory types used in high-performance graphics cards. We’ll use GDDR6 and HBM2 as examples to illustrate the distinctions.
Introduction
Both GDDR and HBM play a crucial role in modern graphics processing. GDDR stands for Graphics Double Data Rate Memory, while HBM stands for High Bandwidth Memory. Let’s dive into their characteristics.
GDDR Memory
 GDDR memory
GDDR memory
As depicted above, GDDR memory typically has a square or rectangular shape. Key manufacturers include Samsung, Hynix, ELPIDA, and Micron.
GDDR5 memory is commonly available in sizes like 512 MB, 1 GB, 2 GB, 4 GB, and 8 GB. The evolution of GDDR memory includes GDDR1 through GDDR5, GDDR5X, and GDDR6.
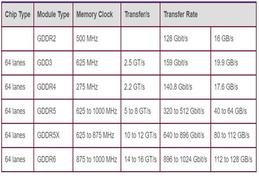
The following table summarizes the features of various GDDR memory types:
 difference between GDDR memory types
difference between GDDR memory types
HBM Memory
 HBM memory
HBM memory
HBM uses a non-planar memory structure with a 3D design, often in a cube or cuboid shape. Multiple memory chips are stacked vertically to form this cube structure. This design results in a smaller footprint, allowing it to be mounted closer to the GPU for faster processing. Hynix and Samsung are key manufacturers of HBM.
The evolution of HBM includes HBM1, HBM2, and HBM3.
The following table outlines the features of different HBM memory types:
 difference between HBM memory types
difference between HBM memory types
GDDR vs. HBM: A Tabular Comparison
Here’s a table highlighting the key differences between GDDR and HBM memory types, using GDDR6 and HBM2 as examples:
| Specifications | GDDR (Example : GDDR6) | HBM (Example : HBM2) |
|---|---|---|
| DRAM density | 16GB (per chip) | 64 GB (per stack) |
| #channels / DRAM package | 2 channels | 8 channels |
| # bits per channel | 16 bits | 128 bits |
| Speed | 16 Gb/s | 2.4 Gb/s |
| Overall bandwidth | 64 GB/s | 307 GB/s |
| Power efficiency | Good | Better than GDDR6 version |
| Cost | Lower than HBM2 | Higher than GDDR6 |
| Packaging | Traditional DRAM on PCB | Uses 2.5D interposer for connectivity between host and HBM2 DRAMs |
Advertisement
 RF
RF