Understanding 5G EN-DC (NR Dual Connectivity)
Advertisement
This page describes 5G EN-DC, also known as 5G NR Dual Connectivity.
In 5G NR, EN-DC stands for E-UTRA-NR Dual Connectivity. 5G EN-DC was introduced in 3GPP Release 15.
The term EN-DC (Evolved-Universal Terrestrial Radio Access-New Radio) refers to E-UTRA NR Dual connectivity. This feature allows a mobile device to exchange data with an NR base station while simultaneously maintaining a connection with an LTE base station. This is possible when tight interworking between LTE and 5G NR base stations is established.

In this dual connectivity mode, the UE (User Equipment) can be simultaneously connected to LTE and NR, or to LTE for the control plane and NR for the user plane. This dual connectivity feature allows the UE to leverage the benefits of both LTE and 5G connectivity at the same time.
Control Plane
- To set up and modify the EN-DC operation, a mobile device must understand both the LTE and NR RRC (Radio Resource Control) control signaling.
- To transport these RRC messages between the network and the mobile device, a set of signaling radio bearers (SRBs) are used:
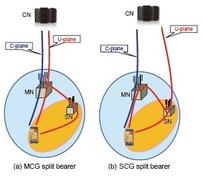
- Master Cell Group (MCG) SRB (SRB1, SRB2)
- Split SRB (SRB1+SRB1S, SRB2+SRB2S)
- Secondary Cell Group (SCG) SRB (SRB3)
User Plane
- When it comes to the user plane, where user data is transported between the network and the mobile device, data radio bearers (DRBs) are used.
- EN-DC supports MCG DRBs, MCG split DRBs, and SCG DRBs.
- An additional data radio bearer, SCG split DRB, has been introduced in EN-DC.
Features of 5G EN-DC | 5G NR Dual Connectivity
The following are the features of 5G EN-DC:
- RRC termination: Both the master node and the secondary node.
- Control Plane termination towards the core network: Only at the master node.
- Supported DRBs: Direct, Split.
- Supported SRBs: MCG SRB (Optionally including NR RRC), Split SRB (Optionally including NR RRC), SCG SRB (including only NR RRC).
- Packet duplication/path switching for split DRBs/SRBs: Path switching support, as well as packet duplication feature (at least in downlink) for both split DRBs and split SRBs.
- Mobility: Master node controls mobility in LTE, while either the master node or the secondary node can control mobility in NR (depending on network configuration).
Advertisement
 RF
RF