WiFi 7: Benefits and Advantages Explained | IEEE 802.11be
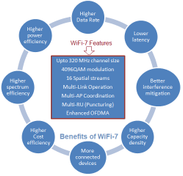
Explore WiFi 7 (IEEE 802.11be), its key features like 320 MHz channels, 4096 QAM, MU-MIMO, and Multi-Link Operation, and the benefits it offers over previous WiFi generations.
Showing 20 posts (Page 4 of 5)
Advertisement

Explore WiFi 7 (IEEE 802.11be), its key features like 320 MHz channels, 4096 QAM, MU-MIMO, and Multi-Link Operation, and the benefits it offers over previous WiFi generations.
Explore WiFi 7's DCM and DCM-DUP, designed to improve signal robustness and coverage by duplicating data across subcarriers or channels for enhanced reliability.

An overview of WiFi 8 (IEEE 802.11bn), the next generation of wireless networking, focusing on planned features like mmWave, multi-link operation, and increased reliability.

Explore the key differences between WiFi boosters and WiFi repeaters, including signal amplification and channel frequency conversion.

Explore the differences between WiFi bridges and access points, and how they extend wireless network coverage. Learn about their functions and key features.

Explore WiFi extender vendors and manufacturers, including TP-Link, Netgear, Linksys, and D-Link. Learn about WiFi extender features and models.
Explore the distinctions between WiFi extenders and routers in terms of coverage, internet connectivity, standalone operation, ports, and cost. Understand how they work together to enhance WiFi.

Explore the advantages and disadvantages of WiFi extenders, including improved performance, easy setup, and extended range, as well as potential drawbacks such as cost and placement issues.

Explore the evolution of WiFi technology, from the original 802.11b to the latest WiFi 6 (802.11ax). Compare speeds, range, and key features across all generations.
Explore WiFi HaLow (WiVi) technology, designed to extend WiFi coverage with low power consumption. Learn about its features, specifications, and applications in IoT networks, adhering to the IEEE 802.11ah standard.

Explore WiFi hotspots for wireless internet access, their setup, and future trends, including WiFi boosters and repeaters for extended coverage.

Explore WiFi network designs for trains, metro stations, and rail tunnels, along with the benefits and technologies involved.

Explore WiFi Quality of Service (QoS) as defined by IEEE 802.11e, including WME/WMM and WSM, to enhance performance for voice, video, and other applications in WLAN networks.
A comprehensive guide to WiFi radio frequency channels for 802.11a/b/g/n, covering 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 4.9 GHz frequency bands.

Learn the fundamentals of WiFi roaming, including internal and external roaming types, how the process works, and the roles of STAs, APs, and AS.

Explore a comprehensive list of WiFi router manufacturers and vendors, covering WLAN standards, specifications, and key features.
Explaining the difference between WiFi signal strengths of -70dB and -50dBm, including definitions of dB and dBm and their significance in wireless communication.

Explore the fundamentals of WiFi sniffers, their operation, and a list of vendors providing WiFi sniffer solutions.
A list of WiFi System on a Chip (SoC) manufacturers and vendors, along with key technical features for IoT applications.

Explore WiFi sensors for temperature, pressure, and humidity. Understand their specifications, accuracy, and applications in wireless data transfer.
Advertisement