
10 WCDMA Interview Questions and Answers
Prepare for your WCDMA/UMTS job interview with these top 10 questions and answers covering key concepts and technologies.
Showing 25 posts (Page 1 of 2)
Advertisement

Prepare for your WCDMA/UMTS job interview with these top 10 questions and answers covering key concepts and technologies.

Explanation of cell re-selection in WCDMA/GSM networks, including trigger conditions, neighbor cell measurements, and the process of switching between WCDMA and GSM cells.
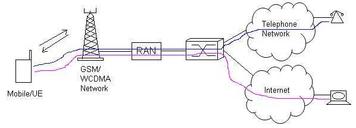
Explore the differences between circuit-switched and packet-switched calls. Understand how they work, their best applications, and call flow examples for GSM and WCDMA networks.
Understand CPRI line rates, including rates 1-10, line bit rates, coding, and transport capacity for WCDMA and LTE AxC.

Explore the differences between Ec/Io and Eb/No in WCDMA, focusing on their measurement points (before and after despreading) and importance in evaluating wireless system performance.

Learn about Inter Radio Access Technology (IRAT) and the IRAT handover process between WCDMA and GSM networks, including message flow and key steps.
Fundamentals of Inter-RAT (IRAT) measurements in multimode modem design, covering GSM, WCDMA, LTE, and TD-SCDMA. UE performs measurements in IDLE/CONNECTED modes for best cell.
Understand the differences between RSCP, Ec/No, and RSSI in WCDMA. Learn how they relate to signal strength and quality in wireless communication.
Explore the key differences between RTWP (Received Total Wideband Power) and RSCP (Received Signal Code Power) in WCDMA/UMTS mobile communication systems.
Explore the key differences between TD-SCDMA, WCDMA, and CDMA2000 3G mobile communication technologies, including their technical approaches, spectrum handling, and regional deployment.

Explore the TD-SCDMA frame structure and physical layer, comparing it to WCDMA. Understand their differences in duplexing, frequency bands, and more.
A comprehensive guide to WCDMA/UMTS timers in User Equipment (UE), covering functions, start/stop conditions, and expiry actions for timers T300 to T317.
Explore the multiple access techniques employed in UMTS (3G), including WCDMA, TD-CDMA, and TD-SCDMA, and learn how they enable efficient spectrum use.

Explore UMTS (3G) technology: network architecture, advantages, disadvantages, and comparisons with GSM (2G) and LTE (4G). Understand its role in mobile communication.
Equations to convert between frequency and UARFCN in UMTS/WCDMA systems. Includes downlink and uplink calculations.

Learn about the WCDMA Acquisition Indicator Channel (AICH), a physical channel carrying Acquisition Indicators (AIs) related to the PRACH signature.

Definition of Collision Detection/Channel Assignment Indicator Channel (CD/CA-ICH) in WCDMA/UMTS systems, including its function and relationship to channel assignment.
Learn the WCDMA cell search procedure used by User Equipment (UE) to synchronize and identify cells in a WCDMA network, including SCH analysis and scrambling code identification.

Learn about WCDMA compressed mode, used to create gaps for mobile devices to perform neighbor cell measurements in UMTS networks. Explore puncturing, spreading factor reduction, and higher layer signaling methods.

Learn about the WCDMA Common Pilot Channel (CPICH), its purpose, and its role in WCDMA/UMTS systems for providing a reference signal for mobile stations.

Learn about the WCDMA CPCH Status Indication Channel (CSICH), its function, and its significance in UMTS networks.

Learn about the WCDMA DPCCH (Uplink Dedicated Physical Control Channel) used in UMTS systems, its structure, and its relationship with DPDCH.

Learn about the WCDMA Downlink Dedicated Physical Channel (DPCH), its characteristics, and its role in transmitting dedicated data to users in UMTS networks.

Learn about the WCDMA Uplink Dedicated Physical Data Channel (DPDCH), its function, and its relationship with DPCCH in UMTS systems.
Overview of WCDMA RF measurements for UE and NodeB, covering transmitter specifications like output power, EVM, and receiver characteristics.
Advertisement