Low Pass FIR Filter Verilog Implementation
Advertisement
Okay, here’s your article converted to Markdown format, incorporating the requirements you specified.
Low Pass FIR Filter Verilog Code
In this implementation, we’re using the same coefficients that were used in the second type of implementation. Specifically, these coefficients are generated from MATLAB, converted into Q-15 format (in hexadecimal representation), and then used in the Verilog code. We’re also using the same input signal of 15 Hz and 100 Hz, converting it into Q-15 format (hexadecimal representation) for use in Verilog.
Verilog Code for Low Pass FIR Filter (Top Module)
module fir_filter(d_out, x, clk, reset, valid);
output signed[15:0] d_out;
input signed [15:0] x;
input clk, reset, valid;
wire signed[15:0] b[0:50];
reg[5:0] coeff_add;
reg signed [31:0] temp0, temp1, temp2, temp3, temp4, temp5, temp6, temp7, temp8,
temp9, temp10, temp11, temp12, temp13, temp14, temp15, temp16, temp17, temp18,
temp19, temp20, temp21, temp22, temp23, temp24, temp25, temp26, temp27, temp28,
temp29, temp30, temp31, temp32, temp33, temp34, temp35, temp36, temp37, temp38,
temp39, temp40, temp41, temp42, temp43, temp44, temp45, temp46, temp47, temp48,
temp49, temp50;
reg signed [15:0] y;
reg signed [15:0] z0, z1, z2, z3, z4, z5, z6, z7, z8, z9, z10, z11, z12, z13, z14, z15,
z16, z17, z18, z19, z20, z21, z22, z23, z24, z25, z26, z27, z28, z29, z30, z31, z32, z33, z34,
z35, z36, z37, z38, z39, z40, z41, z42, z43, z44, z45, z46, z47, z48, z49, z50;
assign b[0] = 16'hFFE8;
assign b[1] = 16'hFF8E;
assign b[2] = 16'hFFAC;
assign b[3] = 16'hFFA0;
assign b[4] = 16'hFFC2;
assign b[5] = 16'h0002;
assign b[6] = 16'h005F;
assign b[7] = 16'h00C6;
assign b[8] = 16'h0119;
assign b[9] = 16'h013B;
assign b[10] = 16'h010F;
assign b[11] = 16'h0087;
assign b[12] = 16'hFFAB;
assign b[13] = 16'hFE9A;
assign b[14] = 16'hFD8F;
assign b[15] = 16'hFCD4;
assign b[16] = 16'hFCB6;
assign b[17] = 16'hFD76;
assign b[18] = 16'hFF37;
assign b[19] = 16'h01F0;
assign b[20] = 16'h056F;
assign b[21] = 16'h0952;
assign b[22] = 16'h0D1E;
assign b[23] = 16'h104F;
assign b[24] = 16'h126F;
assign b[25] = 16'h132E;
assign b[26] = 16'h126F;
assign b[27] = 16'h104F;
assign b[28] = 16'h0D1E;
assign b[29] = 16'h0952;
assign b[30] = 16'h056F;
assign b[31] = 16'h01F0;
assign b[32] = 16'hFF37;
assign b[33] = 16'hFD76;
assign b[34] = 16'hFCB6;
assign b[35] = 16'hFCD4;
assign b[36] = 16'hFD8F;
assign b[37] = 16'hFE9A;
assign b[38] = 16'hFFAB;
assign b[39] = 16'h0087;
assign b[40] = 16'h010F;
assign b[41] = 16'h013B;
assign b[42] = 16'h0119;
assign b[43] = 16'h00C6;
assign b[44] = 16'h005F;
assign b[45] = 16'h0002;
assign b[46] = 16'hFFC2;
assign b[47] = 16'hFFA0;
assign b[48] = 16'hFFAC;
assign b[49] = 16'hFF8E;
assign b[50] = 16'hFFE8;
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (reset)
coeff_add <= 6'd0;
else if (coeff_add == 6'd50)
coeff_add <= 6'd1;
else if (valid)
coeff_add <= coeff_add + 1'd1;
end
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (reset) begin
temp0 <= 16'd0; temp1 <= 16'd0; temp2 <= 16'd0; temp3 <= 16'd0; temp4 <= 16'd0;
temp5 <= 16'd0; temp6 <= 16'd0; temp7 <= 16'd0; temp8 <= 16'd0; temp9 <= 16'd0;
temp10 <= 16'd0; temp11 <= 16'd0; temp12 <= 16'd0; temp13 <= 16'd0; temp14 <= 16'd0;
temp15 <= 16'd0; temp16 <= 16'd0; temp17 <= 16'd0; temp18 <= 16'd0; temp19 <= 16'd0;
temp20 <= 16'd0; temp21 <= 16'd0; temp22 <= 16'd0; temp23 <= 16'd0; temp24 <= 16'd0;
temp25 <= 16'd0; temp26 <= 16'd0; temp27 <= 16'd0; temp28 <= 16'd0; temp29 <= 16'd0;
temp30 <= 16'd0; temp31 <= 16'd0; temp32 <= 16'd0; temp33 <= 16'd0; temp34 <= 16'd0;
temp35 <= 16'd0; temp36 <= 16'd0; temp37 <= 16'd0; temp38 <= 16'd0; temp39 <= 16'd0;
temp40 <= 16'd0; temp41 <= 16'd0; temp42 <= 16'd0; temp43 <= 16'd0; temp44 <= 16'd0;
temp45 <= 16'd0; temp46 <= 16'd0; temp47 <= 16'd0; temp48 <= 16'd0; temp49 <= 16'd0;
temp50 <= 16'd0;
y <= 16'd0;
z0 <= 16'd0; z1 <= 16'd0; z2 <= 16'd0; z3 <= 16'd0; z4 <= 16'd0; z5 <= 16'd0; z6 <= 16'd0;
z7 <= 16'd0; z8 <= 16'd0; z9 <= 16'd0; z10 <= 16'd0; z11 <= 16'd0; z12 <= 16'd0;
z13 <= 16'd0; z14 <= 16'd0; z15 <= 16'd0; z16 <= 16'd0; z17 <= 16'd0; z18 <= 16'd0;
z19 <= 16'd0; z20 <= 16'd0; z21 <= 16'd0; z22 <= 16'd0; z23 <= 16'd0; z24 <= 16'd0;
z25 <= 16'd0; z26 <= 16'd0; z27 <= 16'd0; z28 <= 16'd0; z29 <= 16'd0; z30 <= 16'd0;
z31 <= 16'd0; z32 <= 16'd0; z33 <= 16'd0; z34 <= 16'd0; z35 <= 16'd0; z36 <= 16'd0;
z37 <= 16'd0; z38 <= 16'd0; z39 <= 16'd0; z40 <= 16'd0; z41 <= 16'd0; z42 <= 16'd0;
z43 <= 16'd0; z44 <= 16'd0; z45 <= 16'd0; z46 <= 16'd0; z47 <= 16'd0; z48 <= 16'd0;
z49 <= 16'd0; z50 <= 16'd0;
end else if (valid) begin
z0 <= x; z1 <= z0; z2 <= z1; z3 <= z2; z4 <= z3; z5 <= z4; z6 <= z5;
z7 <= z6; z8 <= z7; z9 <= z8; z10 <= z9; z11 <= z10; z12 <= z11;
z13 <= z12; z14 <= z13; z15 <= z14; z16 <= z15; z17 <= z16; z18 <= z17;
z19 <= z18; z20 <= z19; z21 <= z20; z22 <= z21; z23 <= z22; z24 <= z23;
z25 <= z24; z26 <= z25; z27 <= z26; z28 <= z27; z29 <= z28; z30 <= z29;
z31 <= z30; z32 <= z31; z33 <= z32; z34 <= z33; z35 <= z34; z36 <= z35;
z37 <= z36; z38 <= z37; z39 <= z38; z40 <= z39; z41 <= z40; z42 <= z41;
z43 <= z42; z44 <= z43; z45 <= z44; z46 <= z45; z47 <= z46; z48 <= z47;
z49 <= z48; z50 <= z49;
temp0 <= z0 * b[0]; temp1 <= z1 * b[1]; temp2 <= z2 * b[2]; temp3 <= z3 * b[3]; temp4 <= z4 * b[4];
temp5 <= z5 * b[5]; temp6 <= z6 * b[6]; temp7 <= z7 * b[7]; temp8 <= z8 * b[8]; temp9 <= z9 * b[9];
temp10 <= z10 * b[10]; temp11 <= z11 * b[11]; temp12 <= z12 * b[12]; temp13 <= z13 * b[13]; temp14 <= z14 * b[14];
temp15 <= z15 * b[15]; temp16 <= z16 * b[16]; temp17 <= z17 * b[17]; temp18 <= z18 * b[18]; temp19 <= z19 * b[19];
temp20 <= z20 * b[20]; temp21 <= z21 * b[21]; temp22 <= z22 * b[22]; temp23 <= z23 * b[23]; temp24 <= z24 * b[24];
temp25 <= z25 * b[25]; temp26 <= z26 * b[26]; temp27 <= z27 * b[27]; temp28 <= z28 * b[28]; temp29 <= z29 * b[29];
temp30 <= z30 * b[30]; temp31 <= z31 * b[31]; temp32 <= z32 * b[32]; temp33 <= z33 * b[33]; temp34 <= z34 * b[34];
temp35 <= z35 * b[35]; temp36 <= z36 * b[36]; temp37 <= z37 * b[37]; temp38 <= z38 * b[38]; temp39 <= z39 * b[39];
temp40 <= z40 * b[40]; temp41 <= z41 * b[41]; temp42 <= z42 * b[42]; temp43 <= z43 * b[43]; temp44 <= z44 * b[44];
temp45 <= z45 * b[45]; temp46 <= z46 * b[46]; temp47 <= z47 * b[47]; temp48 <= z48 * b[48]; temp49 <= z49 * b[49];
temp50 <= z50 * b[50];
y <= temp0[30:15] + temp1[30:15] + temp2[30:15] + temp3[30:15] + temp4[30:15] +
temp5[30:15] + temp6[30:15] + temp7[30:15] + temp8[30:15] + temp9[30:15] +
temp10[30:15] + temp11[30:15] + temp12[30:15] + temp13[30:15] + temp14[30:15] +
temp15[30:15] + temp16[30:15] + temp17[30:15] + temp18[30:15] + temp19[30:15] +
temp20[30:15] + temp21[30:15] + temp22[30:15] + temp23[30:15] + temp24[30:15] +
temp25[30:15] + temp26[30:15] + temp27[30:15] + temp28[30:15] + temp29[30:15] +
temp30[30:15] + temp31[30:15] + temp32[30:15] + temp33[30:15] + temp34[30:15] +
temp35[30:15] + temp36[30:15] + temp37[30:15] + temp38[30:15] + temp39[30:15] +
temp40[30:15] + temp41[30:15] + temp42[30:15] + temp43[30:15] + temp44[30:15] +
temp45[30:15] + temp46[30:15] + temp47[30:15] + temp48[30:15] + temp49[30:15] +
temp50[30:15];
end
end
assign d_out = y;
endmodule
Description
Here, the input (x) and output (d_out) are signed 16-bit values in hexadecimal format. valid, clk, and rst are other input signals.
A ROM is declared to store the coefficients (b).
wire signed[15:0] b[0:50];
The ROM has a depth of 51 bits and a width of 16 bits. The 51 coefficients, each 16 bits in size, are stored in this ROM.
Coeff_add is a 6-bit counter. Temp, z, and y are internal signals declared in the code.
The input (x) is loaded into z on each clock edge and then shifted on each edge. These z values are then multiplied by the coefficients and stored in an internal signal called temp.
The upper 16 bits of these temp values are added into another internal signal y, which is finally assigned to the output d_out.
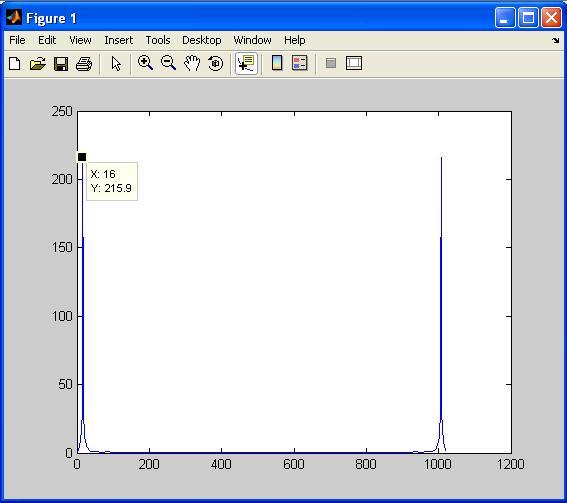
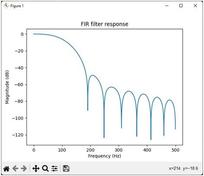
Figure 1. Output signal (d_out) from Verilog code plotted in MATLAB
Therefore, comparing the output waveforms obtained from the MATLAB code and the Verilog code, we can conclude that the two outputs are almost the same.
In summary, the Low Pass FIR filter was implemented in MATLAB using its built-in functions and the FDA tool, and also implemented using Verilog.
Advertisement
 RF
RF