Analog Devices ADCs: An Overview of Features and Applications
Advertisement
Analog Devices is a well-known name in the electronics industry, and their Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) are particularly popular. Recently, they launched a new series of ADCs, further solidifying their position in the market.
Analog Devices ADCs are known for their features such as high speed, low cost, and low power consumption. As the acronym suggests, an ADC converts analog signals into a digital format.
The Crucial Role of ADCs
The ADC serves as a vital bridge between the analog and digital worlds.
- Analog World: Think of the RF (Radio Frequency) domain, where signals exist as electromagnetic waveforms transmitted through the air.
- Digital World: This is where signals are processed in digital form, often using Digital Signal Processing (DSP) techniques.
Analog Devices offers a wide selection of ADCs, each designed for specific applications. Choosing the right ADC depends on several key factors. Analog Devices often provides evaluation boards or reference circuits to help designers integrate their ADCs.
Key Factors for ADC Selection
When selecting an Analog Devices ADC, consider these parameters:
- Throughput Rate (SPS): How many samples can the ADC convert per second?
- Number of Channels: How many analog inputs can the ADC handle simultaneously?
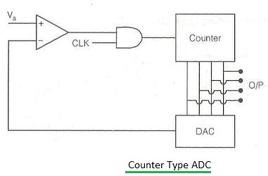
- Circuit Architecture: The internal design of the ADC. Common types include Sigma-Delta, SAR (Successive Approximation Register), and Pipelined.
- Power Dissipation: How much power does the ADC consume?
- Analog Input Type: Does the ADC accept differential or single-ended analog inputs?
About Analog Devices: A Legacy of Innovation
Founded in 1965, Analog Devices has consistently focused on innovation across various engineering disciplines. They are a global leader in designing, manufacturing, and marketing a broad range of products used in analog, mixed-signal, and DSP circuits, which in turn find their way into countless electronic products.
Analog Devices products cater to a diverse range of applications, including:
- Aerospace and defense
- Automotive
- Building technology
- Communications
- Consumer products
- Energy
- Healthcare
- Instrumentation and measurement
- Motor and power control
- Process control and industrial automation
- Security and surveillance
It’s fair to say that Analog Devices has a presence in almost every field of engineering.
Analog Devices Product Portfolio
Their product range is extensive and includes:
- Amplifiers
- A to D and D to A converters
- Audio/video products
- Clock and timing products
- MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems)
- Optical components
- RF and Microwave components
- Processors
- DSPs (Digital Signal Processors)
- Sensors
- Switches
- Multiplexers
Website: www.analog.com
Advertisement
 RF
RF