HIPERLAN Tutorial: Understanding HIPERLAN/1 and HIPERLAN/2
Advertisement
This tutorial covers the basics of HIPERLAN (HIgh PERformance Radio LAN), including its two main types: HIPERLAN/1 and HIPERLAN/2. We’ll explore the HIPERLAN/2 frame structure, its protocol stack, and delve into the Physical (PHY) and Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol layers.
Introduction
HIPERLAN is a set of standards defined by ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) as an alternative to IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi). These specifications are managed by BRAN (Broadband Radio Access Network). There are four main HIPERLAN standards:
- HIPERLAN/1: Radio LAN operating in the 5.15 to 5.3 GHz frequency band, with a range of approximately 50 meters. It achieves a maximum data rate of 23.5 Mbps and supports mobility up to 10 m/s.
- HIPERLAN/2: Operates in the 5.1 to 5.3 GHz band, offering a short range (50 to 100 meters) and data rates exceeding 20 Mbps. It also supports mobility up to 10 m/s.
- HIPERACCESS: Utilizing the 5.1 GHz to 5.3 GHz band, HIPERACCESS provides a range of up to 5000 meters and data rates greater than 20 Mbps in stationary mode.
- HIPERLINK: Operates in the 17.1 to 17.3 GHz band, with a range of up to 150 meters and data rates reaching 155 Mbps in stationary mode.
HIPERLAN/2 Frame Structure
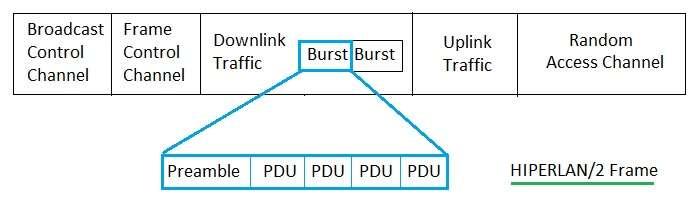
Fig-1: HIPERLAN/2 Frame
The basic frame structure in HIPERLAN/2 comprises several key elements:
- Broadcast: Used for transmitting information to all devices in the network.
- Frame Control: Contains control information for managing the frame.
- Downlink: Carries data from the access point to mobile terminals.
- Uplink: Transmits data from mobile terminals to the access point.
- Random Access: Used by mobile terminals to request access to the network.
HIPERLAN/2 uses a burst transmission format, where each burst consists of a preamble and data fields (Protocol Data Units or PDUs).
HIPERLAN/2 Protocol Stack

Fig-2: HIPERLAN-1 and HIPERLAN-2 protocol stack
Figure 2 illustrates the protocol stacks for both HIPERLAN/1 and HIPERLAN/2.
HIPERLAN/1 Protocol Stack:
As depicted, HIPERLAN/1 has two main layers:
- Physical Layer (PHY): Handles the physical transmission of data.
- Data Link Layer: Responsible for error-free transmission of data frames. It further consists of two sublayers:
- Logical Link Control (LLC): Provides an interface to higher-layer protocols.
- Medium Access Control (MAC): Controls access to the shared wireless medium.
A sublayer called the Channel Access and Control (CAC) Layer exists between the PHY and MAC layers.
HIPERLAN/2 Protocol Stack:
The HIPERLAN/2 protocol stack includes:
- Physical Layer (PHY): Similar to HIPERLAN/1, it handles the physical transmission of data.
- Data Link Control (DLC) Layer: This layer is further subdivided into three sublayers:
- MAC: Medium Access Control
- LLC: Logical Link Control
- RLC: Radio Link Control
- Convergence Layer: Adapts higher-layer protocols to the HIPERLAN/2 DLC layer.
PHY Layer Modulation and Coding Rates
The PHY layer supports the following modulation and coding rates:
| Modulation-code rate | Data rate (Mbps) |
|---|---|
| BPSK-1/2 | 6 |
| BPSK-3/4 | 9 |
| QPSK-1/2 | 12 |
| QPSK-3/4 | 18 |
| 16QAM-9/16 | 27 |
| 16QAM-3/4 | 36 |
| 64QAM-3/4 | 54 |
Advertisement
 RF
RF

