VSAT NMS (Network Management System) Tutorial
Advertisement
This tutorial explains the NMS (Network Management System) used for monitoring and controlling Hub Station and VSAT subsystems. It focuses on star configuration VSAT-based satellite applications.
As shown in the figure below, there are two main parts of the NMS: local NMS and Remote NMS. The local NMS monitors and controls (M&C) subsystems at their respective locations, either at the Hub station or at the VSAT. The Remote NMS at the Hub station takes care of M&C of the remote VSATs.
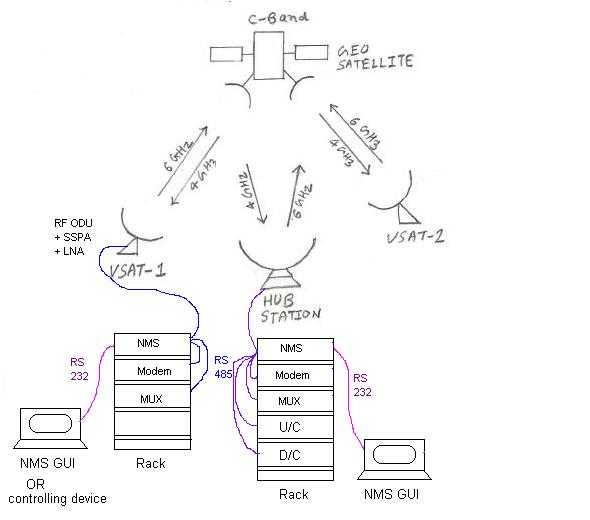
Usually, the following subsystems are available at the Hub station:
- Satellite Modems and modem switch-over unit
- Upconverters and Upconverter switch-over unit
- Downconverters and Downconverter switch-over unit
- LNA and LNA switch-over unit
- HPA and HPA switch-over unit
- MUX with switch-over unit
- NMS controller Unit
- NMS GUI software running on a PC
Typically, the following subsystems are available at the VSAT:
- MUX
- MODEM
- RF ODU
- LNA
- PA
- NMS controller
The switch-over unit helps switch from one active unit to a hot standby unit in case of a fault/failure in the active working unit. The NMS controller at the Hub and VSAT consists of microcontroller hardware and software logic and will interface with respective subsystems as mentioned. All the subsystem manufacturers usually build a protocol into the firmware of the device so that the device can be remotely monitored and controlled.
The NMS GUI software at the Hub station interfaces with the NMS controller at the Hub.
The following are the NMS protocols used at the VSAT and Hub station.
NMS Protocol at VSAT/Hub
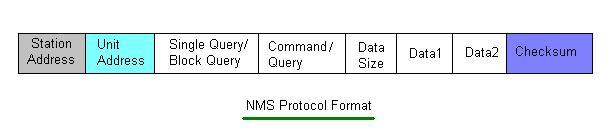
As shown in the figure, the NMS protocol consists of the following fields:
- Station Address: This is the VSAT address.
- Unit Address: This is the subsystem address, i.e., MUX/Modem/RF ODU/SSPA/LNA. For example,
0x65is used for ODU,0x01for Modem, and0x6afor MUX. - Single query/block query: This distinguishes between a single query or a block query.
- Command/Query: This field indicates whether the packet is a command to set some parameters or a query to obtain some parameter of the unit address (subsystem address). There are different fields defined at this place to indicate different functions; for example,
0xccfor query,0xaafor command, and0xbbfor response from remote, etc. - Data Size: This is the size of the data fields.
- Data 1 and data 2: These are the data fields carried in the packet.
- Checksum: This helps in error detection and is usually equal to .
Advertisement
 RF
RF






