Network Security Basics: A Tutorial
Advertisement
Network security refers to the practice of protecting computer networks and their infrastructure from unauthorized access, attacks, and other potential threats. It encompasses a range of technologies, processes, and security policies designed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and resources within a network. The goal of network security is to create a secure environment that safeguards sensitive information, prevents unauthorized access, and maintains the overall functionality of the network.
Why is Security Needed?
Security has become essential due to the widespread use of the internet in our daily lives. Initially, the internet was developed for connectivity purposes. Now, all critical information related to banking, business correspondence, money transactions, and online purchasing happens with the use of the internet.
Hence, it is very important to protect subscriber personal information, confidential data, passwords, and credit or savings card information (used for online purchasing), etc. Today, the internet is evolving very fast, and the use of application-specific online content has become predominant on various networks. Security companies are working on different ways to handle security-related aspects.
Types of Security
Security can be divided into three types: computer security, network security, and internet security.
- Computer security: It is related to the collection of tools developed to protect data available on the computer.
- Network security: It is related to protecting data during their transmission.
- Internet Security: It is related to protecting data during their transmission over a collection of interconnected networks (i.e., the internet).
Attack Sources
There are two attack source types: active attack and passive attack.
- Active Attack: Involves writing data to the network to steal the identity of the traffic sender and other information. Active attacks include spoofing, ARP poisoning, smurf attacks, SQL injection, buffer overflow, etc.
- Passive Attack: Involves reading data from the network to breach confidentiality. Passive attacks include port scanning, eavesdropping, reconnaissance, etc.
Network Attack Types
As shown in Figure 1, there are three ways to sniff the network: internal sniffer, external sniffer, and wireless sniffer. Sniffing can be run on all the layers of the OSI stack.
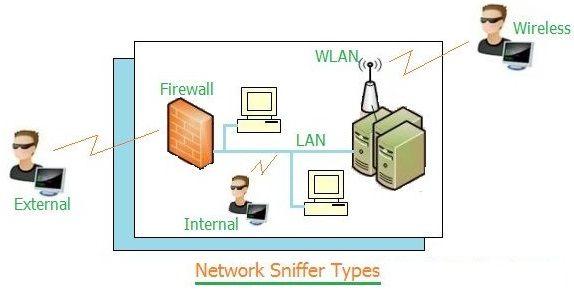
- Internal Sniffer: A hacker can run tools on the LAN to capture the network traffic directly.
- External Sniffer: A hacker can attack through the firewall from outside the LAN to steal network information. This is possible with the use of spoofing techniques and analysis of intercepted network packets.
- Wireless Sniffer: A hacker simply sits nearby to the wireless network and penetrates it to hack the network information.
Packet sniffer software tools designed to capture and analyze network-related issues are being utilized by hackers.
Layered Security and Mitigation Methods
The TCP/IP packet contains information required to establish the network connection. It contains source IP address, destination IP address, port numbers, sequence numbers, protocol type, etc. All these fields are very important for the network layer of the OSI stack to function properly.

As mentioned, the TCP/IP protocol basically helps in reliable packet transmission over ethernet. It does not provide any mechanism to ensure network data security. It is the responsibility of the upper network layers to ensure the packet is not tampered with over the transmission path. Figure 2 depicts OSI layers and what information at each layer hackers can steal by way of sniffing.
Let us understand points to mitigate network security attacks:
- Avoid using insecure protocols like basic HTTP authentication and telnet.
- If you have to use an insecure protocol, try tunneling it through something to encrypt the sensitive data.
- Run ARPwatch.
- Try running tools like sniffdet and Sentinel to detect network cards in promiscuous mode that may be running sniffing software.
- Use wireless networks which have built-in security algorithms such as WEP, WPA etc.
- Use a very strong password consisting of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Do not reveal user-ID to anyone.
- Use secured application layer security protocols such as HTTPS, PGP, SMIME, etc.
Algorithms
Various algorithms and protocols exist at the hardware and software level in order to provide efficient network security. These include cryptography, symmetric key algorithms (DES, 3DES, AES, RC4, RC6, Blowfish), block and stream cipher, etc.
Wireless Network Security Considerations
Wireless networks are evolving quite rapidly in the internet infrastructure. The common wireless networks are based on WLAN, zigbee, Bluetooth, GSM, 3G, LTE, z-wave, etc. Security in such wireless networks involves protecting data transmitted over wireless connections (indoor, outdoor) from unauthorized access, interception, and hacking.
Following security considerations are essential to prevent the hacking of wireless networks.
- Strong authentication and encryption methods should be used. WPA3 or WPA2 methods are employed in wifi networks. In cellular wireless networks, AKS (Authentication and Key Management) and AES techniques are used.
- Change default usernames and passwords for wireless routers or APs (Access Points).
- Implement IDPS (Intrusion Detection and Prevention System) solutions that can monitor wireless network traffic for suspicious activities and block or alert network administrators about potential threats.
- Use RADIUS for strong authentication, especially in enterprise environments.
- Ensure physical access to wireless APs and routers is restricted to authorized personnel. Physical tampering could compromise security.
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments on your wireless network. This will help in identifying weaknesses and in addressing potential risks.
Conclusion
Overall, network security involves protecting data transmitted over wired (e.g., Ethernet, fiber optic) as well as wireless connections (e.g., Wi-Fi, cellular) from interception, unauthorized access, and hacking. There is no single security measure that is completely foolproof. Hence, a layered approach which combines multiple security strategies is the most effective way to secure your network and prevent hacking.
Advertisement
 RF
RF