Cloud Storage Security Explained: Mechanisms and Concerns
Advertisement
As we know, cloud storage services offer numerous benefits, including:
- Scalability
- No upfront investment costs
- Pay-as-you-go pricing
- Accessibility from anywhere
However, despite these advantages, cloud environments also present certain threats:
- Unknown exposure risks
- Loss of control over data and infrastructure
- Reliance on a fast and reliable network connection
- Inherent risks associated with outsourcing sensitive data
- Limited customization options
These factors raise significant security concerns for both cloud customers and service providers.
In the context of cloud storage security, customers are primarily concerned with protecting their outsourced programs and data. This includes preventing attacks originating from the provider itself and safeguarding against attacks targeting the provider by other tenants sharing the same infrastructure.
Cloud service providers, on the other hand, are focused on protecting their infrastructure and maintaining a consistent level of service quality for all customers. This involves mitigating abuse by tenants, such as the use of botnets or spamming activities, and preventing tenant-to-tenant attacks.
Cloud Storage Security Mechanisms
Several security mechanisms can be implemented to address these concerns:
- Data at Rest Encryption: Encrypting data while it is stored on the cloud infrastructure.
- Data Authentication/Integrity Protection: Ensuring the authenticity and integrity of data to prevent unauthorized modifications.
- Data Replication: Creating multiple copies of data across different locations for redundancy and disaster recovery.
- Access Control to Data: Implementing strict access controls to limit who can access specific data.
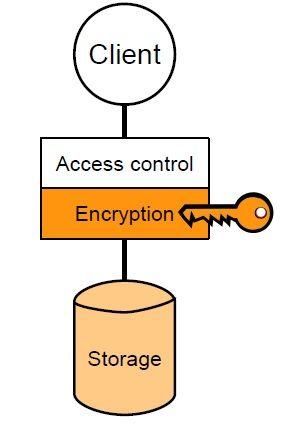
While access control measures exist between the client and the storage server, robust security remains essential. This is because attackers often find ways to bypass these access controls. Encryption shifts the focus of access control to managing access to encryption keys, making it easier to protect sensitive data. This concept is illustrated in Figure 1.
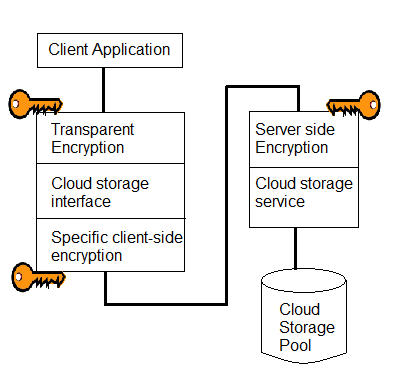
Data encryption can be implemented either on the client-side before uploading data to the cloud or on the cloud service provider’s side.
Advertisement
 RF
RF





