WLAN 802.11ax: Wave 1 vs. Wave 2 Features
Advertisement
This page compares the features of WLAN 802.11ax Wave 1 and Wave 2.
What is WLAN 802.11ax?
Introduction:
- IEEE 802.11ax is the 6th generation of WiFi technology, also known as Wi-Fi 6.
- Due to its high efficiency, it’s sometimes referred to as HEW (High Efficiency WLAN).
- It was developed to address limitations of 802.11ac, such as contention-based uplink access.
- This version of the WLAN standard introduces major features to offer better efficiency, network capacity, performance, power savings, and user experience with reduced latency.
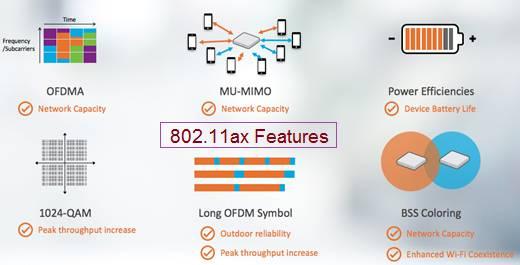
Image Courtesy: Ruckus Networks
- The stable version of the 802.11ax draft 2.0 was released in September 2017. Many chipsets have already been developed based on this version.
- The final version of the standard was planned for release in 2019.
802.11ax Wave 1 Features
The following features were included in the 802.11ax Wave 1 release:
- Downlink and Uplink OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access)
- Downlink MU-MIMO (Multi-User MIMO)
- Target Wake Time (TWT)
- BSS Coloring (Basic Service Set Coloring)
- 20 MHz only operation
802.11ax Wave 2 Features
The following features were included in the 802.11ax Wave 2 release:
- Uplink Multi-User MIMO
- Spatial Re-use
- Long Range 802.11ax
802.11ax Access Point and Client Features
As we know, any WLAN network consists of two elements viz. AP (Access Point) or router and Client devices. The following tables outline the mandatory and optional features planned for incorporation in WLAN 802.11ax APs and client devices.
802.11ax Access Point
| Feature | Mandatory | Optional |
|---|---|---|
| OFDMA | Downlink OFDMA Transmit Uplink OFDMA Receive | |
| MU-MIMO | Downlink MU-MIMO Transmit (if 4+SS) | Downlink MU-MIMO Transmit (if <4 SS) |
| Beamforming | Transmit Beamforming (if 4+SS) | |
| MIMO | SU MIMO Transmit & receive with up to 2xSS | SU MIMO with 3 +SS |
| Bandwidth | 20, 40, 80 MHz operation if supporting 5GHz 20 MHz operation if supporting 2.4 GHz 20 MHz only operation in wideband OFDMA | 160 MHz operation (if supporting 5 GHz) |
| Power Saving | Individual TWT | |
| Network Efficiency | BSS Coloring | Spatial Reuse |
| Operating Mode | Transmit & Receive Operating Mode | |
| Modulation and Coding Scheme | MCS 8, MCS9, MCS10, MCS 11 (256 & 1024 QAM) |
802.11ax Client
| Feature | Mandatory | Optional |
|---|---|---|
| OFDMA | Downlink OFDMA Receive Uplink OFDMA Transmit | |
| MU-MIMO | Downlink MU-MIMO Receive (Upto 4 x SS) | |
| Beamforming | Receive Beamforming | |
| MIMO | SU MIMO Transmit & Receive | |
| Bandwidth | 20, 40, 80 MHz operation if supporting 5 GHz 20 MHz operation if supporting 2.4 GHz | |
| Network Efficiency | BSS coloring | Spatial Reuse |
| Operating Mode | Transmit & Receive Operating Mode | |
| Power Saving | Individual TWT |
 RF
RF


