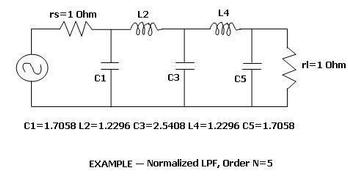
Bias Tee vs. DC Block: Key Differences Explained
Advertisement
This article clarifies the distinction between a Bias Tee and a DC Block, outlining their functions and features to help you choose the right component for your needs.
What is a Bias Tee?

- As shown in the figure above, a Bias Tee allows RF (radio frequency) signals to pass through one port while simultaneously allowing DC signals to pass through another.
- It’s useful for delivering DC voltage or current to RF devices like amplifiers or switches while preventing RF/Microwave signals from interfering on the same line.
- Bias Tees find applications in test and measurement equipment and as a biasing tool in power amplifiers.
Example: The ZFBT-6G+ from Mini-Circuits is a commercially available Bias Tee.
What is a DC Block?

- A DC Block acts as a high-pass filter, blocking DC frequencies and even audio frequencies.
- It’s primarily used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and dynamic range in a system.
Example: The BLK-6+ from Mini-Circuits is a DC Block with an N-type coaxial connector, operating from 10 MHz to 6 GHz. DC blocks with SMA and BNC connectors are also available.
Advertisement
 RF
RF