FDM vs TDM : Difference between FDM and TDM
Advertisement
Introduction : These are two fundamental techniques used to transmit multiple signals over a single communication channel. FDM divides the available bandwidth into separate frequency bands for each signal, while TDM allocates time slots to each signal in a sequential manner. Both methods are widely used in telecommunications, networking and broadcasting, but they differ in implementation, efficiency, and application suitability.
What is FDM?
FDM stands for Frequency Division Multiplexing. In FDM, each signal is modulated onto a unique Radio Frequency (RF) carrier. These carrier frequencies are carefully chosen and spaced apart so that the bandwidths of the signals don’t overlap in the frequency domain. This prevents interference between the signals.
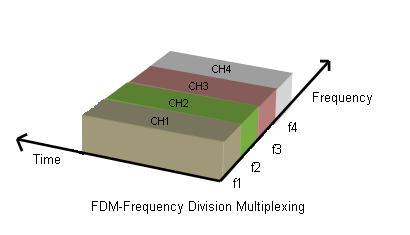
Fig.1 FDM
As illustrated in Figure 1, several signal sources are fed into a multiplexer. Each source modulates a different RF carrier (f1, f2, f3, and f4). Guard bands are added between the RF carriers to further minimize interference between adjacent channels, also known as Adjacent Channel Interference (ACI).
For a deeper dive into the comparisons, it’s useful to refer to the comparison of FDMA vs TDMA vs CDMA.
What is TDM?
TDM stands for Time Division Multiplexing. With TDM, multiple digital signals are transmitted over a single medium by interleaving each signal in time.
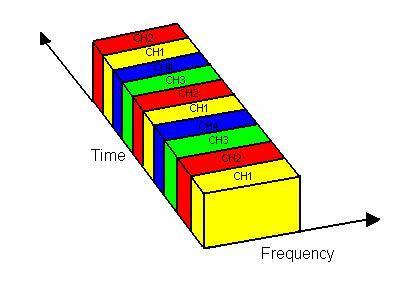
Fig.2 TDM
As shown in Figure 2, four channels, each with a data rate of approximately 2.4 kbps, can be multiplexed onto a single line with a capacity of 9.6 kbps using TDM.
TDM isn’t limited to just digital signals; it can also be used with analog signals. It’s also possible to combine TDM and FDM. In such a hybrid scheme, the frequency spectrum is first divided into channels using FDM, and then each channel is further subdivided into time slots using TDM.
Applications
- TDM: Commonly used in PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) transmission to achieve T1 at a rate of 1.544 Mbps.
- FDM: Widely used in satellite communications, radio broadcasting, HF (High Frequency) radio, and other wireless technologies.
- Both TDM and FDM: Employed in GSM (Global System for Mobile communications) cellular technology. Refer to GSM Frame Structure for more details. The GSM frame structure utilizes FTDMA, which is a combination of FDMA and TDMA.
Conclusion : FDM and TDM serve the same purpose of sharing a single channel among multiple signals but achieve it in different ways. FDM uses frequency separation, while TDM uses time separation. FDM is ideal for analog signals and continuous transmission, whereas TDM suits digital signals and bursty data traffic. The choice between them depends on the nature of the data, synchronization needs and the available bandwidth.
Advertisement
 RF
RF







