AESA Radar: Active Electronically Scanned Array Explained
Advertisement
This page defines AESA radar basics. It includes an AESA Radar block diagram with the principles of its working operation, and the benefits/advantages of AESA radar technology.
What is AESA Radar?
AESA stands for Active Electronically Scanned Array. The radar that uses this type of antenna is known as AESA radar. It’s also referred to as active phased array radar (APAR).
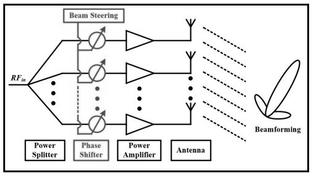
It consists of individual radiating elements (antennas). Each of these antennas is equipped with solid-state Transmit/Receive modules, which include a low noise receiver, a Power Amplifier, and digitally controlled gain/phase elements.
 AESA Radar Block Diagram
AESA Radar Block Diagram
AESA Radar Working Operation
The figure above depicts an AESA radar block diagram. This type of radar utilizes both analog beamforming as well as digital beamforming elements. An array of antenna elements is employed. Both the phase and amplitude of the input signal are controlled before being applied to individual antenna elements.
This allows the beam to be steered in both azimuth and elevation directions. Consequently, the main lobe of the radiation pattern is beamed in the desired direction with the desired directivity.
The phased array antenna used in AESA radar will rotate its radiation pattern with no delay, unlike mechanically steered radar types. Digital control of transmit/receive gain and timing waveforms aids in beam steering.
The width of the beam depends on the number of elements in the antenna array. Smaller size targets are detected by using a large number of elements, as the beam becomes sharper.
Modern AESA radars are often built using thousands of individual elements that are electrically interconnected. This provides a complex antenna structure with improved performance while maintaining reduced size and weight.
AESA Radar Benefits or Advantages
Following are the benefits or advantages of AESA radar:
- Rotates the pattern with no delay.
- Low sidelobes are achieved.
- Significant reduction in antenna radar signature compared to other radar types.
- AESA radar systems are more reliable compared to other radar systems.
- A large, high-voltage power supply is not required, as all the individual modules operate at low power (around 40 or 60 watts).
Advertisement
 RF
RF