NFC: Advantages and Disadvantages of Near Field Communication
Advertisement
Near Field Communication (NFC) has emerged as a popular technology for contactless transactions and device communication. With a simple tap, NFC facilitates seamless data transfer, greatly improving the convenience of mobile payments and information sharing. While NFC boasts unique advantages, it also presents certain limitations. This guide offers an overview of the main benefits and drawbacks of NFC.
What is NFC?
NFC stands for Near Field Communication. As the name implies, it’s used for short-distance data communication between two devices: an initiator (i.e., NFC reader) and a target (i.e., NFC Tag). NFC finds applications in various scenarios, such as data communication between smartphones, verification of authorized personnel in offices and government buildings, and ticket booking.
It operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz with different low data rates, namely 106, 212, or 424 kbps. The NFC tag can be either active or passive, while the NFC reader is always in active mode.
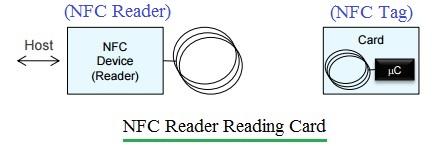
Near Field Communication (NFC) technology enables two NFC-enabled devices, or an NFC device and a passive NFC tag, to communicate wirelessly over short distances, typically less than 10 centimeters. NFC is based on radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, specifically in the 13.56 MHz frequency range.
When two NFC devices are brought into close proximity, they create a magnetic field through electromagnetic induction, allowing data to be exchanged securely and quickly without the need for manual device pairing.
NFC Modes
NFC technology has three main modes of operation:
-
Peer-to-Peer Mode: In this mode, two active NFC devices (like smartphones) exchange information, such as photos, contact details, or links. Both devices generate their own power and actively participate in data transfer.
-
Read/Write Mode: Here, an NFC device reads data from or writes data to a passive NFC tag embedded in posters, cards, or other objects. The passive tag draws power from the electromagnetic field generated by the active NFC device, allowing it to transfer information like URLs or text.
-
Card Emulation Mode: In this mode, an NFC device, like a smartphone, acts like a contactless smart card, allowing it to be used for mobile payments or access control. When placed near a payment terminal or access reader, the device securely transfers information to complete transactions or grant entry.
Advantages of NFC
Here are some of the benefits of NFC:
- It is very convenient for making payments and other transactions using smartphones with a wallet app.
- It’s used for multiple applications across various domains, such as banking, reservations, booking tickets, redeeming offers, and entry/exit passes.
- It benefits both customers and enterprises.
- It provides secure access for students and employees in their premises.
- It offers more security compared to magnetic strip-based debit and credit cards, and often includes PIN verification.
- It doesn’t require search and pair procedures like Bluetooth and other methods to establish connectivity.
- No special software is needed, and it doesn’t require manual configurations and settings.
Disadvantages of NFC
Here are some of the limitations of NFC technology:
- It only works over short distances, about 10-20 cm.
- It offers very low data transfer rates, around 106, 212, or 424 Kbps.
- It can be expensive for companies to adopt NFC-enabled devices.
- It might not be advantageous for all users due to complex procedures compared to other easier options.
- Although more secure than credit/debit card systems, it is not completely risk-free due to the increasing prevalence of mobile hacking, which can provide complete access to smart devices.
- Power consumption is comparatively higher in NFC-enabled devices.
Conclusion
NFC technology simplifies connectivity and enhances convenience in transactions and data sharing. While its short range and security measures make it useful for daily tasks, potential limitations should be considered. Balancing NFC advantages and disadvantages will help you determine whether NFC is an ideal solution for your connectivity needs.
FAQs on NFC: Questions and Answers for Interview
Question-1: What is NFC technology?
Answer-1: NFC (Near Field Communication) is a short-range wireless communication technology that enables devices to exchange data over distances of 10 centimeters or less. It allows for quick and secure connections between devices, making it ideal for applications like mobile payments, data sharing, and access control.
Question-2: What are the advantages of NFC?
Answer-2: NFC offers several advantages, including convenience for quick transactions by simply tapping devices together and enhanced security through encryption and tokenization. It also supports contactless payments, making it popular in mobile wallets.
Question-3: What are the disadvantages of NFC?
Answer-3: NFC has disadvantages, such as its limited range, which typically extends only a few centimeters, and compatibility issues, as not all devices support NFC technology. Additionally, NFC can be slower than other wireless technologies for larger data transfers and is susceptible to interference in crowded environments.
Question-4: How does NFC work for mobile payments?
Answer-4: For mobile payments, NFC-enabled devices communicate with payment terminals by bringing them close together. The user authenticates the payment on their device, which then transmits encrypted payment information to the terminal, completing the transaction quickly and securely.
Question-5: Can NFC be used for data sharing between smartphones?
Answer-5: Yes, NFC allows for data sharing between smartphones, such as contact information, photos, and links. Users can simply tap their devices together to initiate the transfer, making it a fast and convenient way to share data.
Question-6: Are NFC transactions secure?
Answer-6: Yes, NFC transactions are generally secure. They use encryption and tokenization to protect sensitive information. However, users should ensure that their devices have proper security measures in place, such as passwords and biometric authentication, to further enhance security.
Question-7: What are some common applications of NFC?
Answer-7: NFC is widely used in various applications, including:
- Mobile payments (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay)
- Access control (e.g., key cards for secure entry)
- Public transportation (e.g., contactless ticketing)
- Smart posters (e.g., accessing additional information by tapping a poster)
- Data sharing between devices (e.g., sharing photos or contacts)
Advertisement
 RF
RF