Human Intranet: Definition, Benefits, and Advantages
Advertisement
This page explains the basics of a “Human Intranet” and its potential benefits. A Human Intranet is essentially a network of sensors that connect the human brain with the body.
In simpler terms, it’s a connection between our biological brain and implanted electronics on the body. This concept is illustrated in Figure 1 and is often referred to as a Brain-Machine Interface (BMI).
 Figure 1: Illustration of a Human Intranet
Figure 1: Illustration of a Human Intranet
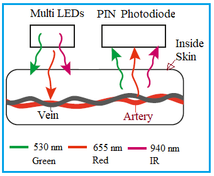
The electronic devices acting as sensors in a Human Intranet are known as “neural motes.” These motes can be attached to clothing or even placed beneath the skin, depending on the application.
These implanted sensors gather information and transmit it wirelessly to a central PC. This PC processes and analyzes the data to evaluate various body-related performance parameters. As shown in the figure, communication between nodes can occur through ultrasound, wireless signals, or wired connections.
The system is generally comprised of the following key components:
- Wrist-worn control unit or hub
- Neural recording unit (EEG/ECoG)
- Energy-starved sensor patches
- Sensor interrogation nodes
- Actuator unit controlled by neural feedback and the Hub
Benefits and Advantages of a Human Intranet
Here are some key benefits of a Human Intranet:
- Heart Rate Monitoring: It can be used to continuously monitor heart rate.
- Glucose Level Measurement: It allows for easy and frequent measurement of glucose levels.
- Painless Health Monitoring: It provides a less invasive method for obtaining detailed health information. This helps in treating critical, long-lasting diseases.
- Treatment of Previously Untreatable Diseases: Human Intranet technology opens doors to treat diseases that were once considered incurable.
- Reduced Treatment Costs: As neural motes become more affordable, the cost of treatment is expected to decrease over time.
Advertisement
 RF
RF