Virtual IP Address vs. Logical IP Address: Key Differences
Advertisement
This page compares virtual IP addresses and logical IP addresses, outlining the key differences between them.
Virtual IP Address
A virtual IP address (VIP) can be configured manually or obtained using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). The most common use case for VIPs is in high-availability scenarios, such as with VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol).
In a VRRP configuration, this address is shared among multiple routers. This way, if the primary (master) router fails, a backup router can seamlessly take over, providing uninterrupted internet connectivity to hosts on the LAN.
VIPs can be in either IPv4 or IPv6 format. The “master” router (or the IP address owner) will often have its virtual IP address configured to be the same as its real, logical IP address. Backup routers are configured with the same virtual IP address as the master.
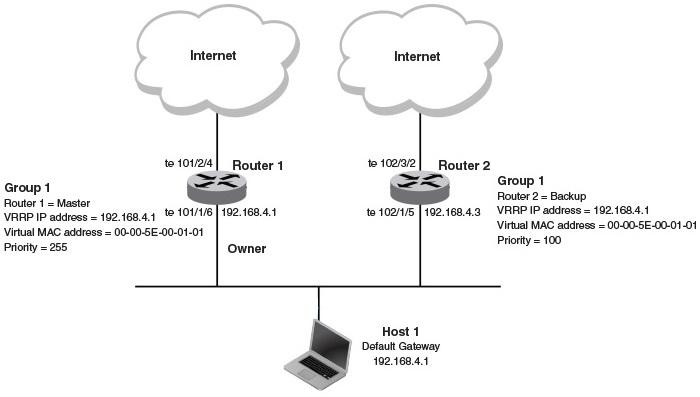
Refer to the VRRP protocol documentation for more in-depth information.
Logical IP Address
A logical IP address is simply a normal IP address assigned to a computer. These addresses exist in either 32-bit (IPv4) or 128-bit (IPv6) formats.
The logical IP address is contained within the IP header of a network packet. It’s used to route the packet across the internet to its intended destination.
Advertisement
 RF
RF



