PTMP vs. Mesh Networks: Key Differences Explained
Advertisement
This article breaks down the differences between PTMP (Point-to-Multi-Point) and Mesh (Point-to-Point) network architectures. Both are commonly used but offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. Often, a combination of both is leveraged in system deployments to harness their respective strengths.
What are PTMP and Mesh Networks?
- PTMP (Point-to-Multi-Point): A network where a single central node transmits data to multiple receiving nodes.
- Mesh (Point-to-Point): A network where multiple nodes connect directly to each other, forming a mesh-like structure.
PTMP (Point-to-Multi-Point) Networks
Figure 1 illustrates a PTMP network used in satellite communication.
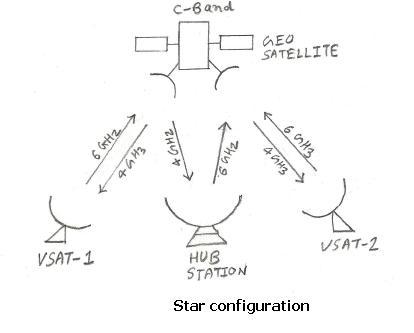
In this setup, a hub station transmits a signal to a satellite, which then relays or broadcasts it to multiple remote VSATs. Another example is TV broadcasting, where a signal is transmitted to a satellite and then relayed to many disc TV antennas across a large geographical area.
Typically, in a PTMP setup, one central station (like a hub or TV station) transmits point-to-point to another station (like a satellite), which then broadcasts to multiple points (VSATs or disc antennas).
Advantages of PTMP
- Large Area Coverage: Effective for reaching a broad geographical region.
- Centralized Access: Complete control and access to the entire network from a single location.
- Easy Upgrades: System upgrades can be implemented efficiently from the central point.
- Simplified Maintenance and Monitoring: Monitoring and maintenance are easier due to the centralized nature.
Disadvantages of PTMP
- Line-of-Sight (LOS) Challenges: Obstructions in urban areas can hinder signal transmission.
- Single Point of Failure: Failure at the central hub can disrupt the entire network. Redundant systems are often needed as a backup.
- High Initial Costs: Site acquisition and construction for the central hub can be expensive.
Mesh (Point-to-Point) Networks
Figure 2 shows a typical Mesh network architecture.
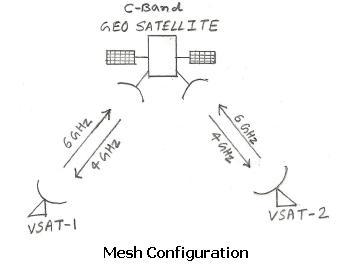
In a mesh network, all stations communicate directly with each other without relying on a central device (like a hub or TV station). This configuration is also known as a PTP (Point-to-Point) network.
Advantages of Mesh Networks
- Easy Deployment: Relatively simple to install and set up.
- High System Capacity: Can handle a large volume of data traffic.
- Suitable for NLOS Environments: Works well in areas with obstructions and dense urban environments.
- Resilience: Failure of one station does not affect the others. The network can re-route traffic.
Disadvantages of Mesh Networks
- Complex Management: Maintenance and monitoring can be challenging due to the distributed nature of the network. Centralized access is typically not available.
- Cost-Ineffective in Sparsely Populated Areas: May not be economically viable for areas with low population density.
- Distributed Asset Management: Requires managing many distributed assets, which can be complex.
Advertisement
 RF
RF




