IPsec Advantages and Disadvantages
Advertisement
This page covers the advantages and disadvantages of IPsec. It mentions IPsec benefits (advantages) and IPsec drawbacks (disadvantages). It also provides IPsec basics.
What is IPsec? - Introduction
- IPsec is used in VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), which provide a private, secured connection between a client and a server over the public internet.
- Various tunneling protocols exist at layer-2 and layer-3 to provide secured connections. IPsec operates at layer-3, the network layer.
- RFC 4301 defines the IPsec architecture, as depicted in Figure 1.
- The IPsec protocol provides security services for traffic at the IP layer, protecting the IP layer and upper layers from hacking.

Figure 1: IPSec Architecture
- There are two IPsec modes: tunnel mode and transport mode.
- Tunnel mode: The entire IP packet is encrypted first, becoming the data part of a new, larger IP packet. This is used in IPsec site-to-site VPN topologies.
- Transport mode: The IPsec header is inserted into the original IP packet. No new packet is created. This is used in remote access VPN topologies.
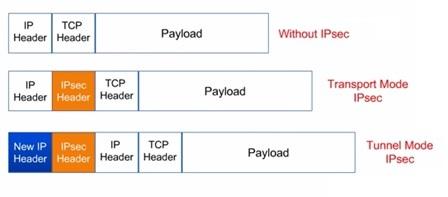
Figure 2: IPSec Transport Mode vs IPSec Tunnel Mode
Figure 2 depicts IPsec packet formats.
As we know, normal IP packets do not have any inherent security. Moreover, there is no way to verify the following:
- The claimed sender is the true sender.
- The data has not been modified during transit.
- The data has not been viewed by a third party.
Benefits or Advantages of IPsec
The following are the benefits or advantages of IPsec:
- The first drawback (sender authentication) is overcome by authentication. Signatures and certificates help in this regard.
- The second drawback (data integrity) is overcome by integrity checks. Checksums calculated by routers at each end of the tunnel or hash values of the data to be transported help in this regard.
- The third drawback (confidentiality) is overcome by encryption of data. This is achieved by key management and other IPsec protocols.
- IPsec provides security without any modifications to user computers.
- It can work independently of applications. All application data are routed with IP, making them IPsec compatible.
- With the help of the IP layer, IPsec can be applied to networks of all sizes, from LAN to WAN.
- As IPsec functions at a very low network level, its performance is not affected by users, applications, or protocols.
- IPsec allows per-flow or per-connection-based security, enabling very fine-grained security control.
- As mentioned, it provides seamless security to application and transport layers (ULPs).
Drawbacks or Disadvantages of IPsec
The following are the disadvantages of IPsec:
- For small packet transmissions, network performance diminishes due to the large overhead used by IPsec.
- IPsec is complex due to the number of features and options. Higher complexity increases the probability of weaknesses or holes in the protocol. For example, IPsec is weak against replay attacks (or playback attacks), where valid data transmissions are fraudulently repeated or delayed.
- IPsec can defeat the purpose of a firewall because firewalls are based on pre-configured rules that are encrypted by IPsec. This can be overcome by using a firewall along with an IPsec gateway, which decrypts the encrypted firewall data.
- It is more difficult to implement for individual users on multi-user machines.
- Other drawbacks include policy management, local policy configuration, supportability, and increased performance requirements.
Advertisement
 RF
RF