Edge Computing: 5 Advantages and Disadvantages
Advertisement
Introduction: Edge computing is an emerging paradigm in information technology that brings data processing and storage closer to the source of data generation, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. By minimizing the distance data must travel, edge computing reduces latency, improves real time decision-making, and enhances the efficiency of applications such as the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, healthcare monitoring and smart cities.
In cloud computing, the cost of CPU usage, storage and bandwidth can be significant. Edge computing addresses this by analyzing data closer to its source, determining whether it needs to be sent to the cloud or not. This significantly reduces costs by minimizing storage requirements. This approach is the fundamental concept behind edge computing. Bandwidth is also generally cheaper at the edge compared to the cloud.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is essentially an optimization of cloud computing, moving the computation closer to the data source where the data is generated. It involves delivering computing capabilities to the network’s edge to improve performance, reduce operating costs, and enhance the reliability of applications and services. Edge computing leverages “Edge Nodes” where data processing takes place.
The following figure illustrates a typical edge computing architecture.
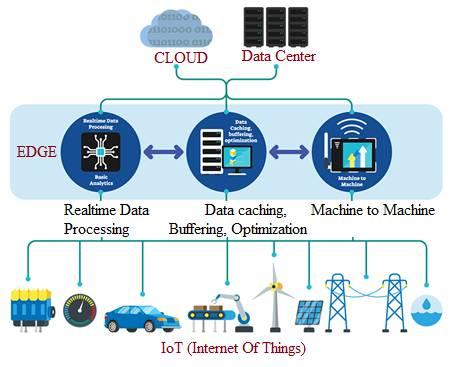
Image Courtesy: IEEE
Edge computing finds applications in various scenarios, including:
- City Surveillance: Utilizing CCTV cameras to identify traffic issues and criminal activities.
- IoT (Internet of Things): Analyzing data from IoT devices at the network’s edge before sending it to a data center or cloud.
- Self-Driving Cars: Enabling complete autonomy without human intervention.
- Industry 4.0: Facilitating advanced automation and data-driven decision-making in industrial settings.
- Healthcare and Financial Transactions: Providing lower latency for time-sensitive operations.
Advantages of Edge Computing
Following are some of the key benefits of Edge Computing.
- Simplifies internal communication by physically wiring assets to intelligent Programmable Automation Controllers (PACs), enabling efficient data collection, analysis, and processing.
- Pushes intelligence, processing power, and communication capabilities directly into devices like PACs through edge gateways or appliances.
- Helps in deciding whether to send data to the cloud or store it locally for further analysis.
- Can function independently of cloud or fog computing.
- Suited for systems requiring minimal human interaction, like driverless cars.
- Offers very low latency, making it ideal for time-critical applications like finance and healthcare.
Disadvantages of Edge Computing
Following are some of the drawbacks or limitations of Edge Computing.
- Less scalable compared to fog computing.
- Not cloud-aware in its basic implementation.
- Operations might not easily extend to both IT and OT (Operational Technology) teams.
- Typically does not support resource pooling.
- Often interconnected through proprietary networks with custom security measures and limited interoperability.
- Limited to a smaller number of peripheral layers.
Conclusion: Edge computing represents a significant step forward in how data is processed and delivered, offering solutions to the limitations of traditional cloud computing. Its ability to provide low latency, real time insights makes it especially valuable in applications requiring immediate responses. However, the technology is not without challenges, including infrastructure costs, potential security risks and scalability concerns.
Advertisement
 RF
RF



