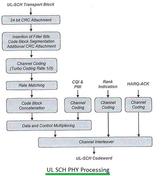
LTE Code Block Concept in the Physical Layer
Advertisement
This article explains the concept of code blocks within the LTE (Long-Term Evolution) physical layer, focusing on how transport blocks are segmented and processed for efficient transmission.
Code Block Segmentation in Detail
In LTE, a Transport Block (TB) is divided into smaller units called code blocks before undergoing channel coding and rate matching. This process, known as code block segmentation, is essential for efficient error correction and transmission.
LTE uses two code block sizes:
- Minimum Code Block Size: 40 bits
- Maximum Code Block Size: 6144 bits
These sizes are carefully chosen to align with the Turbo interleaver module of the CTC (Convolutional Turbo Code) encoder.
When is segmentation needed?
If the input Transport Block length exceeds the maximum code block size (6144 bits), segmentation becomes necessary. The Transport Block is then split into multiple code blocks, each adhering to the maximum size constraint.
CRC Attachment:
Each resulting code block is appended with a 24-bit Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC). This CRC is calculated in a manner similar to the Transport Block CRC, providing error detection capabilities at the code block level.
Filler Bits:
To ensure compatibility with the Turbo interleaver, filler bits (zeros) are added to the beginning of some code blocks. These filler bits pad the code block size to match a valid set of Turbo interleaver block sizes.
No Segmentation Required:
If the input block size is already less than or equal to the maximum code block size (6144 bits), no segmentation is performed, and only a single code block is generated.
Handling Blocks Smaller Than the Minimum Size:
If the input block (B) is smaller than the minimum code block size (40 bits), filler bits (zeros) are added to the beginning of the code block until it reaches the required 40-bit length.
Code Block Concatenation
After rate matching, the outputted code blocks are concatenated back together, forming a single stream of data ready for transmission.
Advertisement
 RF
RF