LTE Carrier Aggregation: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advertisement
This page covers the advantages and disadvantages of LTE Carrier Aggregation. LTE stands for Long Term Evolution.
Introduction
The concept of carrier aggregation was introduced in LTE Release-10. Carrier aggregation refers to the combination of multiple carriers. This increases the bandwidth proportionate to the number of aggregated carriers and the bandwidth per carrier.
Increased bandwidth helps in achieving higher data rates. LTE Release 10 supports aggregation of up to 5 Component Carriers (CCs). In LTE, five bandwidths are supported: 1.4, 3, 5, 10, 15, and 20 MHz. Hence, a maximum total aggregated bandwidth of 100 MHz can be achieved.
With LTE Release 13, about 32 CCs can be aggregated, which significantly increases bandwidth and, therefore, the data rate.
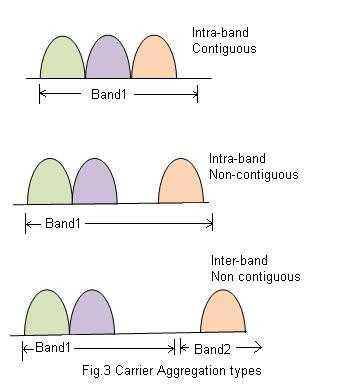
Figure-1 Carrier Aggregation types
Advantages of Carrier Aggregation
The following are the advantages of carrier aggregation:
- It helps in increasing bandwidth allocation to User Equipments (UEs, or mobile subscribers) by combining the CCs. 3GPP Release 10 supports aggregation of 5 CCs, while Release 13 supports aggregation of 32 CCs. This helps in achieving high downlink and uplink data rates.
- Network operators have the option to deploy the network in one of three types: Intra-band contiguous, intra-band non-contiguous, and inter-band non-contiguous.
- Carrier Aggregation enables the aggregation of unlicensed and licensed carrier frequency spectrum, utilizing unlicensed bands.
- Dynamic flow switching across CCs is possible with Carrier Aggregation.
- Expanded coverage is no longer a trouble for telecom carriers, as they can scale the carriers as needed.
- Carrier Aggregation can be applied to both Time Division Duplexing (TDD) and Frequency Division Duplexing (FDD) topologies.
- The Carrier Aggregation feature helps improve network efficiency for network operators, resulting in an optimized user experience.
Disadvantages of Carrier Aggregation
The following are the disadvantages of carrier aggregation:
- Multiplexers are needed at the transmit end to combine the component carriers, and RF filters are needed at the receive end to separate out the component carriers. These extra devices increase costs for equipment and device manufacturers and increase system complexity. SAW (Surface Acoustic Wave) and BAW (Bulk Acoustic Wave) type RF filters are used.
- Power Amplifiers (PAs) and Switches are specially designed to meet the requirements of Carrier Aggregation based RF systems. For example, highly linear PAs are used for intra-band CA. Switches with higher isolation between ports are used.
- Testing this feature requires complex test and measurement hardware and software. This increases the cost for smartphone and equipment manufacturers to avail of the test service/equipment. Test and measurement companies such as Anritsu, Rohde & Schwarz, and Agilent provide T&M solutions to test this feature.
- It increases the cost of smartphones due to the extra requirement of hardware components, e.g., switches and filters in the RF chain.
Advertisement
 RF
RF