Bit Rate vs. Baud Rate: Key Differences in Data Communication
Advertisement
This article breaks down the concepts of bit rate and baud rate, explaining their differences and how they relate to each other in data communication.
Introduction
In the world of data communication, digital data, whether it’s text, numbers, images, audio, or video, is represented using bits (ones and zeros). This binary representation is the foundation of how information is stored and transmitted.
To transmit this data, we use signal elements, which are physical representations of the data bits. Line coding techniques (like unipolar, polar, and bipolar encoding) are used to convert these bits into digital signals suitable for transmission.
The ratio (‘r’) defines the number of data elements carried by each signal element. Consider these examples:
- r = 1/2: One data element is mapped per two signal elements.
- r = 2: Two data elements are mapped per one signal element (e.g., QPSK modulation).
- In 16QAM, four binary bits are mapped using one symbol.

The figure above illustrates the relationship between data elements and signal elements.
Bit Rate Explained
- Bit rate, also known as data rate, represents the number of data elements (bits) transmitted per second.
- It’s measured in bits per second (bps), or sometimes kilobits per second (kbps) or megabits per second (Mbps).
- A higher bit rate generally means faster data transmission.
Baud Rate Explained
- Baud rate, also called signal rate, represents the number of signal elements transmitted per second.
- It’s measured in baud. It can also be referred to as pulse rate, modulation rate, or symbol rate.
- A lower baud rate can be beneficial for conserving bandwidth.
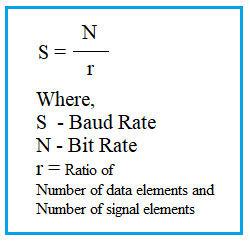
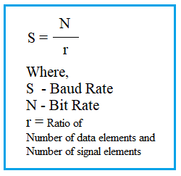
The relationship between bit rate and baud rate is crucial:
Bit Rate = Baud Rate x Number of bits per baud
Let’s look at some examples:
-
Example 1 (AM modulation): If each signal element carries one binary bit, then r = 1. In this case, Symbol rate (Baud rate) = Bit Rate.
-
Example 2 (16-QAM modulation): Here, one symbol represents 4 bits, so r = 4. Thus, S = N/4, meaning the bit rate (N) is four times the baud rate (S).
Bit Rate vs. Baud Rate: A Tabular Comparison
| Parameters | Bit Rate | Baud Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transmission of the number of binary bits per second. | Transmission of the number of signal elements (symbols) per second. |
| Unit | bps, kbps, Mbps, Gbps | Baud, Kbaud, Mbaud |
| Formula | Bit rate = Baud rate x Number of bits per baud | Baud rate = Bit rate / Number of bits per baud |
| Relationship | A higher bit rate means faster data transmission. | A lower baud rate means less bandwidth used for data transmission. |
| Example Application | Raw data (before modulation) is measured in bits per second. | Modulated data (after modulation) is measured in symbols per second (baud). |
Advertisement
 RF
RF