DAS (Distributed Antenna System): 5 Advantages and Disadvantages
Advertisement
Introduction: As the name implies, a DAS is a network of spatially separated antennas. These antennas are connected to a transport medium, typically coaxial cable or fiber optic cable, to provide wireless services within a home or building. A distributed antenna system can be driven by a direct connection to a cellular base station, a cellular tower, or a repeater.
The growth of mobile data and cellular usage has made it essential to install more small cells to handle the rapid increase in mobile subscribers. This has opened the door for distributed antenna systems (DAS). In a DAS, it’s not necessary to install a completely new cell phone tower; instead, antennas are mounted on existing towers.
The figure below illustrates various cell phone tower types designed for specific applications.

In DAS technology, multiple antennas are mounted on a single cell tower to relay frequencies in different bands for the same or different technologies (GSM, CDMA, LTE, etc.). These antennas can be installed by a single telecom operator or by multiple operators on the same cell tower.
DAS technology is commonly used in the following venues:
- Multi-tenant high-rise buildings in close proximity.
- Corporate offices of Fortune 500 companies.
- University campuses.
- Manufacturing and production facilities.
- Hospitals and healthcare facilities.
- Casinos.
- Stadiums or sports venues.
- Religious places (e.g., Kaaba at Mecca).
- Convention centers.
- Hotels.
- Federal or local Government facilities.

DAS involves the deployment of various antenna configurations to enhance or extend the coverage of cellular signals both inside and outside of structures. Therefore, DAS is used as both an indoor and outdoor antenna system. Some systems cover just a few floors, while others cover many floors or areas of a building or campus.
Advantages of Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS)
Following are the benefits of using a Distributed Antenna System:
- Increased Capacity: DAS increases the capacity of a cellular tower by using multiple antennas for single or multiple bands and technologies (GSM, CDMA, LTE, LTE-Advanced, etc.).
- Scalability: Cell towers in a DAS setup can be upgraded with additional antennas as needed in the future. This makes it easy to manage increasing bandwidth demands.
- Multi-Carrier Support: DAS can provide internet connectivity in a single area by multiple telecom carriers.
- Reduced Interference: It helps to overcome RF interference because the same coverage is achieved with lower transmit powers from various antennas.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Customers experience fewer dropped calls or blocked calls, and network access failures are less frequent.
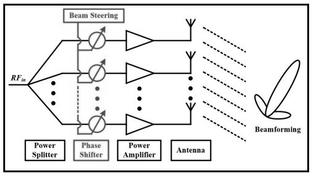
- Enhanced Communication Speed: DAS helps improve communication speed using MIMO/Beamforming techniques.
Disadvantages of Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS)
Following are the drawbacks of using a Distributed Antenna System:
- High Cost: DAS systems require multiple radio heads (RRH) and connections to a central hub using fiber optic cables, making them very expensive.
- Complex Cable Management: DAS technology requires complex cable management in the backhaul part of the system.
- Difficult Upgrades: Upgrading a DAS can be more challenging compared to small cell networks. Small cell networks often use over-the-air (OTA) upgrades, while DAS technology may require the replacement of systems (e.g., base stations and radio heads).
Conclusion: Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) provide an effective solution for enhancing wireless coverage and capacity in areas where traditional cell towers fall short, such as large buildings, stadiums, and underground facilities. By distributing signals through multiple antennas, DAS ensures consistent connectivity and improved signal strength. Despite higher deployment and maintenance costs, its advantages like better indoor coverage, scalability, and support for multiple carriers; make DAS a vital infrastructure component in modern wireless communication networks.
Advertisement
 RF
RF