Adaptive Antennas: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advertisement
Adaptive antennas, also known as smart antennas or adaptive arrays, are advanced antenna systems that dynamically adjust their radiation patterns to optimize signal reception and transmission. These antennas use signal processing algorithms to monitor the radio environment and adapt their characteristics, such as beam direction and shape, to improve communication quality and efficiency.
Adaptive antennas are widely used in modern wireless communication systems, including cellular networks, Wi-Fi, radar, and satellite communications.
Key Features of Adaptive Antennas
-
Beamforming: Adaptive antennas use beamforming techniques to focus the radio signals in specific directions rather than broadcasting uniformly. This enhances the signal strength toward intended users and reduces interference from other directions.
-
Direction of Arrival (DoA) Estimation: Adaptive antennas can estimate the direction from which incoming signals are arriving, allowing them to optimize their response and improve communication quality.
-
Null Steering: This technique enables the antenna to create nulls (areas of minimal radiation) in the direction of interfering signals, thereby reducing the impact of interference.
-
Dynamic Adjustment: The antenna system continuously monitors the environment and adjusts its beam patterns in real-time to respond to changes, such as user movement or varying signal conditions.
-
Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO): Adaptive antennas are often used in MIMO systems, where multiple antennas are employed at both the transmitter and receiver ends to enhance data throughput and reliability.

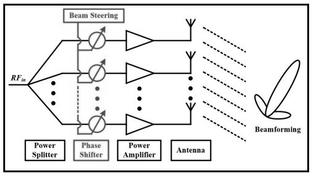
The figure depicts adaptive antenna array (AAS) in analog beamforming technique.
Advantages of Adaptive Antennas
Following are the benefits or advantages of Adaptive Antennas:
-
By focusing the signal directly toward the intended user, adaptive antennas improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), leading to clearer and more reliable communication.
-
Adaptive antennas can extend the coverage area by directing beams toward areas with weaker signals and by managing multiple users simultaneously, increasing the capacity of the network.
-
With beamforming and null steering capabilities, adaptive antennas can significantly reduce interference from unwanted signals, improving the overall network performance.
-
By directing energy precisely and using the available spectrum more effectively, adaptive antennas increase spectral efficiency, allowing for higher data rates within the same bandwidth.
-
Adaptive antennas can dynamically adjust to changing conditions, making them suitable for environments with high user mobility, such as in vehicles or moving crowds.
-
Focused beams mean that less power is wasted in directions where it’s not needed, improving the energy efficiency of the communication system.
Disadvantages of Adaptive Antennas
Following are the drawbacks or disadvantages of Adaptive Antennas:
-
The advanced signal processing algorithms and multiple antenna elements required for adaptive antennas increase the complexity and cost of the system, making them more expensive than traditional antennas.
-
The real-time adjustments and signal processing required by adaptive antennas demand powerful processing capabilities, which can lead to higher energy consumption and increased system complexity.
-
The performance of adaptive antennas can be influenced by the surrounding environment, such as obstacles, multipath effects, and user movement, which may complicate the adaptation process.
-
Adaptive antennas require precise calibration and ongoing maintenance to function optimally, which can increase operational costs and complexity.
-
The process of continuously adjusting the beam patterns may introduce slight delays, which can be critical in time-sensitive applications, such as high-frequency trading or certain industrial controls.
-
Although adaptive antennas reduce interference from unintended sources, they can still be vulnerable to deliberate jamming or spoofing attacks, which can disrupt their ability to properly direct signals.
Conclusion
Adaptive antennas provide significant advantages in enhancing communication quality, reducing interference, and increasing network capacity. However, their complexity, cost, and the need for sophisticated processing and maintenance are important considerations that must be managed to fully leverage their potential in modern communication systems.
Advertisement
 RF
RF