5G vs WiFi 6: Key Differences and Comparisons
Advertisement
As wireless technologies evolve, 5G and WiFi 6 have emerged as game changers in the connectivity landscape. But what sets them apart? This article delves into the key differences between 5G and WiFi 6, comparing their speed, range, applications, and more. Whether you’re setting up a smart home or seeking seamless mobile connectivity, understanding these distinctions can help you make the right choice.
5G is the successor to 4G LTE cellular technology, whereas WiFi 6 is the successor to 802.11ac technology. Cellular technologies from 1G to 5G follow 3GPP specifications. WiFi technologies follow IEEE 802.11 WLAN PHY/MAC specifications.
5G is a cellular network technology that enables ultra-fast mobile connectivity, supporting wide area coverage and high mobility. WiFi 6, the latest iteration of WiFi technology, offers improved speed, efficiency, and capacity for local wireless networks, making it perfect for home or office environments.
What is 5G technology?
5G technology has been developed as per 3GPP Rel. 15 and beyond. The 5G NR (New Radio) initial specifications were finalized by 3GPP in December 2017. 5G has been deployed initially in non-standalone mode and later in standalone mode.
In non-standalone mode, the control mechanism is leveraged using the existing 4G LTE network, and data transfer takes place using the 5G network infrastructure. In standalone mode, both control and data mechanisms are handled by the 5G network itself without any dependency on the legacy 4G LTE network.

The figure depicts the overall network architecture of the 5G NR system. As shown, it consists of UE (User Equipment), NG-RAN (Radio Access Network), and 5G Core.
5G wireless systems support different frequency bands below 6 GHz and above 6 GHz in the mmWave range. It supports higher bandwidth (~ 1Gbps or higher), low end-to-end latency (~ 1-5 ms), and higher data rates (Peak: 1-10 Gbps, Cell Edge: 100 Mbps).
Advantages of 5G
Following are the benefits of the 5G cellular system:
- 5G supports excellent mobility due to its roaming support.
- During data congestion due to an increased number of subscribers, 5G can offload traffic to indoor WiFi networks.
- 5G offers a 10x improvement in throughput, a 10x reduction in latency, a 10x improvement in connection density, a 3x improvement in spectrum efficiency, and a 100x improvement in traffic capacity and network efficiency.
- Dynamic beamforming features help overcome path loss at higher mmWave frequencies.
- Higher bandwidth and data rates can be achieved using carrier aggregation and massive MIMO.
What is WiFi 6?
It is the 6th generation of WiFi technology, which is based on recent IEEE 802.11ax specifications. WiFi is also called WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network). To establish a WiFi 6 link, one requires WiFi 6 compliant routers.

As shown in the WLAN architecture, the WiFi 6 router is connected to the internet using a broadband connection. All the WiFi 6 mobile phones and other compliant devices connect with the WiFi 6 router.
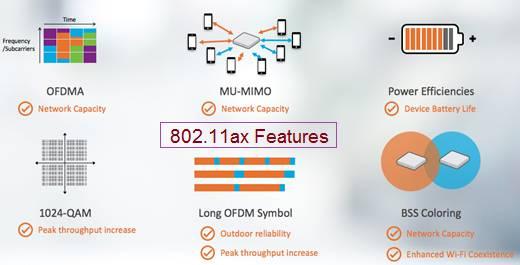
The figure depicts some of the advanced features introduced in the WiFi 6 system. The features are as follows:
- MU-MIMO
- Beamforming
- 1024-QAM modulation
- Longer size OFDM symbol
- Higher number of spatial streams (up to 8)
- Uplink resource scheduling without any contention unlike 802.11ac etc.
- BSS coloring
- OFDMA
- Longer battery life etc.
Advantage of WiFi 6
Following are the benefits of the WiFi 6 system:
- WiFi 6 provides 40% higher peak data rates and a 4x improvement in network efficiency.
- WiFi 6 based scheduling mechanisms help to reduce overhead and latency. Moreover, multiple users can transmit simultaneously.
- WiFi 6 client devices consume less power due to the use of TWT (Target Wake Time) features, and hence it enhances battery life.
- WiFi 6 offers higher security due to the use of the WPA3 protocol.
- WiFi 6 uses long symbol duration outdoors and short symbol duration indoors.
- Co-channel interference is mitigated due to the use of BSS color coding.
Difference between 5G and WiFi 6
The following table compares 5G and WiFi 6 on various parameters.
| Specifications | 5G | WiFi 6 |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Cellular | WLAN |
| Standard | 3GPP Rel. 15 and beyond | IEEE 802.11ax |
| Operating frequency | Sub 1 GHz, 1 to 6 GHz, Greater than 6 GHz in the millimeter wave range at 28 GHz and 40 GHz | 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz both |
| Spectrum | Licensed | Unlicensed |
| Speed | Greater than 1 Gbps | Higher than 5G, About 600 Mbps with 80MHz/1 SS, About 9.6 Gbps with 160 MHz/8SS (11ac version gives about 7 Gbps with 160 MHz, 8 SS). |
| Range | 5G small cells support 10-100 meters range based on their types such as femtocell, pico cell, and microcell. 5G mmWave base station covers 2 meters (in indoor) and 300 meters (in outdoor). | Greater than 100 meters, Beamforming features improve range by 4 times than 802.11ac (i.e., WiFi 5) version. |
| Maturity of the technology and its penetration | It is at nascent stages and will take a few years to reach the current stage of 4G LTE deployments | It has already matured and has deep penetration into our homes, enterprises, residential communities, and commercial establishments |
| Cost of deployment | Expensive | Cheaper |
| IT administrators | Not required | Required, as WiFi networks are installed and managed by them |
| Security | 5G cellular connections are more secure compared to unknown WiFi connections. 5G users are exposed to security risks during the process called WiFi offloading. 5G will be as secure as 4G LTE today. 5G supports multiple authentication and key management features. | WiFi 6 supports WPA3 security protocols to provide high security. |
| Mobility | Higher | Lower than 5G |
| Application | Outdoors | Indoors |
Conclusion
While 5G and WiFi 6 both enhance connectivity, their strengths lie in different areas. 5G offers expansive mobility and high-speed internet on the go, while WiFi 6 provides efficient and reliable connectivity in local environments. By evaluating your specific requirements, you can decide which technology is better for your needs. Both 5G and WiFi 6 have their unique features, and hence they will coexist.
Advertisement
 RF
RF


