5G Protocol Stack: Layer 1, Layer 2, and Layer 3 Explained
Advertisement
This page provides an overview of the 5G Protocol Stack, detailing the functions of Layer 1, Layer 2, and Layer 3. In 5G, Layer 1 is the PHYSICAL Layer, Layer 2 includes MAC, RLC, and PDCP, and Layer 3 is the RRC layer.
Figure 1 illustrates the 5G Protocol Stack, showcasing both the User Plane and Control Plane protocol layers.

5G Layer 1 | 5G PHYSICAL Layer
The 5G Layer 1, also known as the PHYSICAL (PHY) Layer, is responsible for the following functions:
- Error detection on the transport channel and indication to higher layers
- FEC encoding/decoding of the transport channel
- Hybrid ARQ soft-combining
- Rate matching of the coded transport channel to physical channels
- Mapping of the coded transport channel onto physical channels
- Power weighting of physical channels
- Modulation and demodulation of physical channels
- Frequency and time synchronization
- Radio characteristics measurements and indication to higher layers
- Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) antenna processing
- Transmit Diversity (TX diversity)
- Digital and Analog Beamforming
- RF processing
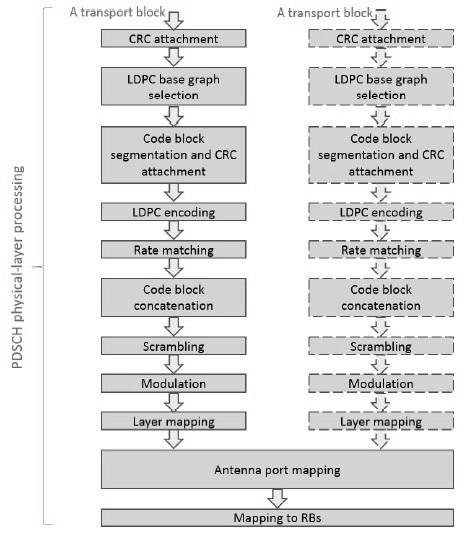
The 38.200 series of documents define processing of PDSCH and PUSCH channels through the PHYSICAL layer modules.
5G Layer 2 | 5G MAC, RLC, PDCP Layer
The 5G Layer 2 encompasses the MAC, RLC, and PDCP sublayers.
MAC Sublayer Functions:
- Beam management
- Random access procedure
- Mapping between logical channels and transport channels
- Concatenation of multiple MAC SDUs belonging to one logical channel into transport block (TB)
- Multiplexing/demultiplexing of 5G-MAC SDUs belonging to one or different logical channels into/from transport blocks (TB) delivered to/from the physical layer on transport channels
- Scheduling information reporting
- Error correction through HARQ
- Priority handling between logical channels of one UE
- Priority handling between UEs by means of dynamic scheduling
- Transport format selection
- Padding

RLC Sublayer Functions:
- Transfer of upper layer PDUs
- Error Correction through ARQ (only for AM data transfer)
- Reordering of 5G-RLC data PDUs (only for UM and AM data transfer)
- Duplicate detection (only for UM and AM data transfer)
- Protocol error detection (only for AM data transfer)
- 5G-RLC SDU discard (only for UM and AM data transfer)
- Segmentation (only for UM and AM data transfer)
- Resegmentation (only for AM data transfer)
- 5G-RLC re-establishment

PDCP Sublayer Functions (User Plane):
- Transfer of user data
- In-sequence delivery of upper layer PDUs at 5G-PDCP re-establishment procedure for 5G-RLC AM
- Duplicate detection of lower layer SDUs at 5G-PDCP re-establishment procedure for 5G-RLC AM
- Retransmission of 5G-PDCP SDUs at mobility in connected mode for 5G-RLC AM
- Ciphering and deciphering (Note: Only AES shall be mandatory)
- Timer-based SDU discard in uplink
PDCP Sublayer Functions (Control Plane):
- Ciphering and Integrity Protection (Note: Only AES shall be mandatory)
- Transfer of control plane data


5G Layer 3 | 5G RRC Layer
The 5G Layer 3, known as the RRC Layer, has the following responsibilities:
- Broadcasting of system information to NAS and AS.
- Establishment, maintenance, and release of RRC connection.
- Security, including key management.
- Establishment, configuration, maintenance, and release of point-to-point radio bearers.
- Mobility functions along with cell addition and cell release.
- UE measurement reporting, control of UE reporting, UE-based mobility.
- NAS direct message transfer to/from NAS from/to UE.
References:
- TS V5G.300
- TS V5G.201
- 3GPP TS 38.212 (Multiplexing and channel coding), TS 38.321 (MAC specifications), TS 38.322 (RLC specifications)
- Website: https://5gtf.net
Advertisement
 RF
RF

