Millimeter Wave (mmWave) Link Budget Calculator
This page discusses the Millimeter Wave Link Budget Calculator, also known as the mm-wave link budget calculator, and its underlying formula. It uses the example of a 60 GHz 802.11ad millimeter wave system for its calculations.
Introduction:
Any frequency ranging from 30 GHz to 300 GHz falls under the millimeter wave (mm-wave) frequency spectrum. A system utilizing frequencies within this range is considered an mm-wave system. One such system is the IEEE 802.11ad based system, also known as WiGig.
The RF link budget is crucial for understanding the transmit power needed to achieve the appropriate Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and receiver power for optimal system performance. This takes into account path loss and other attenuation factors, like oxygen attenuation, vapor attenuation, and rain attenuation. By adjusting the transmit power, you can observe the resulting received signal level and SNR based on the input path loss.
Millimeter Wave Link Budget Calculator and 802.11ad Example
Here’s an example of how the Millimeter Wave Link Budget Calculator works:
INPUTS:
- Tx power = 12 dBm
- Tx Gain = 38 dB
- Tx line loss = 0 dB
- Operating frequency = 60 GHz
- Path length = 0.7 Km
- Rx Gain = 38 dB
- Rx line loss = 0 dB
- Rx Noise figure= 10 dB
- BW = 2000 MHz
- Temp (degreeC) = 25 °C
- Vapor attenuation = 0 dB/Km
- Oxygen attenuation = 14.9 dB/Km
- Rain attenuation = 9.175 dB/Km
OUTPUTS:
- Transmit EIRP = 50 dBm
- Free Space Path Loss = 124.91 dB
- Receive Noise Floor = -70.85 dBm
- Receive Signal Level = -53.77 dBm
- SNR = 17.08 dB
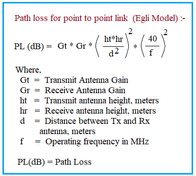
Formula/Equations used in Millimeter Wave Link Budget Calculator or 802.11ad link budget

The mm wave Link Budget formula/equations above are used in this Millimeter Wave (mm-wave) Link Budget Calculator.
RF Link Budget Calculator
Refer to the RF Budget Calculator with its image and equations mentioned below:


 RF
RF