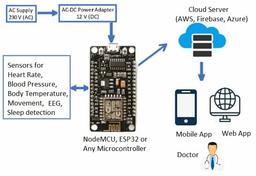
IoT-Based Water Quality Monitoring System Architecture
Advertisement
This document describes an IoT-based Water Quality Monitoring System Architecture suitable for lakes, rivers, and other water bodies. It highlights the disadvantages of manual and nodal network methods and the advantages of an IoT-based system.
Introduction
Water quality is declining due to environmental changes and man-made pollution. This makes it essential to measure water quality in various water bodies regularly. This helps reduce water pollution and save aquatic life. The following methods are used to monitor water quality at regular intervals:
- Manual Method
- Nodal Network Method
- IoT (Internet of Things) Method
Manual Method of Water Quality Monitoring
In the manual method, water samples are collected by hand from different parts of the water body. These samples are sent to a laboratory for analysis of parameters such as pH, dissolved oxygen, conductivity, and chloride content.
The limitations (drawbacks or disadvantages) of the manual method include:
- It’s difficult to collect samples from the entire water body area.
- The cost of analysis is very high.
- Lab testing takes time, so results don’t reflect real-time water quality due to delays.
- The process is time-consuming because of slow manual data collection from different locations.
- The method is prone to human errors.
Nodal Network Method of Water Quality Monitoring
In this method, wireless sensor nodes are installed in various regions of a river. These sensors collect data and upload it to cloud storage via the internet. The analysis team initially fixes the location of sensors and their position inside the water.
The limitations (drawbacks or disadvantages) of the Nodal network method include:
- The system is less effective because sensors are installed deep inside the water, and their positions are fixed.
- The sensors are very expensive. Their maintenance cost is also high, leading to higher costs for the regulatory body.
- Sensors that rely on a power source may need to be replaced if they malfunction.
- Mounted sensors can be damaged during natural disasters or by aquatic animals.
IoT-Based Water Quality Monitoring System

- In the IoT-based method, a water boat housing an ESP32 board with water sensors is used. The ESP32 provides Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities. To enable GSM/GPRS functionality, a GSM/GPRS board (SIM800A) is interfaced with the ESP32 via UART. In contrast, if using an Arduino Uno, one must interface a separate Wi-Fi/BLE module, as the Arduino doesn’t have a built-in Wi-Fi or BLE chip.
- The water sensor kit includes various sensors to measure water quality, such as pH sensors, temperature sensors, conductivity sensors, and dissolved oxygen sensors.
- The data collected by sensors from different locations in the water body (e.g., river or lake) is uploaded to a cloud storage server using Wi-Fi or GSM.
- The data is analyzed using machine learning techniques, and reports are generated in various formats.
- End-users can monitor reports and results from water samples collected from various locations using a mobile or web app.
- GPS coordinates of the collected samples are integrated into the reports to show the level of contamination at specific locations.
Benefits or Advantages of IoT-Based Water Quality Monitoring System
The benefits or advantages of an IoT-based Water Quality Monitoring System include:
- The boat is mobile, allowing for easy collection of a large number of samples from different locations in less time.
- It is easy to maintain the IoT-based water quality monitoring system as all the electronic boards are available in the boat itself.
- The system is inexpensive because the hardware and software costs are low.
- Machine learning techniques make it easy to plot the data collected in various formats for proper analysis.
- Cloud storage platforms, such as Adafruit and Azure, allow immediate and wireless storage of sensor data to robust servers.
Advertisement
 RF
RF