Transistor as a Switch: Application Note
Advertisement
This application note provides a basic description of a transistor used as a switch.
Transistor Switch Circuit
The following circuit diagram illustrates an NPN transistor used as a switch:
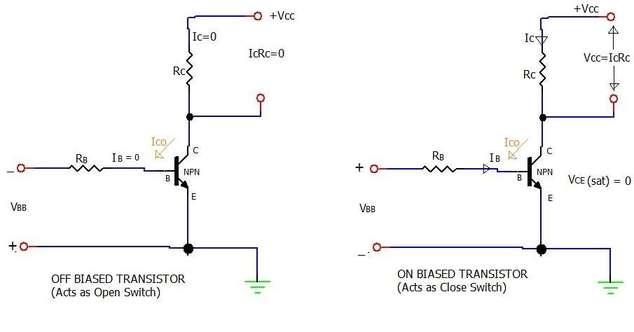
Figure: NPN transistor circuit used as switch.
Transistors as Electronic Switches
As we know, a circuit that can turn on or off current is known as a switching circuit. A transistor can be used effectively as an electronic switch.
Operating a transistor as a switch involves operating it in either the cut-off or saturation mode.
- Cut-off Mode: When the transistor is in cut-off, it behaves like an open switch, preventing current flow.
- Saturation Mode: When the transistor is saturated, it behaves like a closed switch, allowing maximum current flow.
The DC voltage applied to the transistor terminals is referred to as the bias voltage.
NPN Transistor Operation
- Cut-off Region: Applying a negative voltage to the base of this NPN transistor forces it into the cut-off region.
- Saturation Region: Applying a positive voltage to the base of this NPN transistor forces it into the saturation region.
When the transistor is switched on, the collector current () increases from to . Conversely, when the transistor is switched off, decreases from to .
Due to , which is the minority carrier leakage current, the transistor does not function as an ideal switch. This leakage current introduces a small amount of current flow even when the transistor is supposed to be off.
Advantages of Transistor-Based Switches
For high-speed switch applications, transistor-based switches are superior to other switch types due to their fast switching speeds and reliability.
Advertisement
 RF
RF






