Microstrip Filter Structures: Basics and Types
Advertisement
This article explores the fundamentals of microstrip filter structures and delves into various types, including stub-loaded, stepped impedance, directly coupled, parallel coupled, interdigital, and combline designs. Microstrip filters are built using these transmission line sections printed on a dielectric substrate. Their layout and coupling style determine frequency response, size and performance.

Figure 1: Microstrip filter structure types
Let’s examine each of these microstrip filter structures in detail.
Stub-Loaded Microstrip Filter : It uses open circuited or short circuited stubs connected with main transmission line. Shunt stubs connected either at specific points along the main line. Typical use cases are Compact filters, tunable notches and bandstop filters.
Stepped Impedance Filter : A cascade of transmission lines alternating between high impedance and low impedance sections.
Each “step” alternates between wide (low-Z) and narrow (high-Z) lines. Line lengths and impedance ratios are carefully designed to achieve desired filter shapes. Typical use cases are Bandpass filters and harmonic suppression.
Directly Coupled Resonator Filter : Resonators are placed in series and directly coupled. Straight transmission lines with small spacing or direct contact between them. Coupling controlled by gap width. Typical use case include narrowband and wideband bandpass filters.
Parallel Coupled Line Filter : Two or more microstrip lines are placed side by side with tight spacing to enable electromagnetic coupling. Each resonator is a quarter-wavelength long at center frequency. Coupling depends on the distance and length of parallel sections. Typical use cases include Bandpass filters, especially for moderate bandwidths.
Interdigital Filter : Multiple resonators arranged in a finger like, alternating manner with grounded or open ends. Open circuited or shorted resonators placed alternatively. Resemble “interlaced fingers” on the layout. Typical use cases include wideband filters and its compact size.
Combline Filter : Similar to interdigital, but one end of every resonator is shorted to ground and resonators are capacitively loaded. Short circuited stubs connected to a common ground. Additional capacitors at the open end for tuning. Typical use cases are High-Q narrowband filters, especially in compact or low profile systems.
Microstrip-Based RF Filter Design
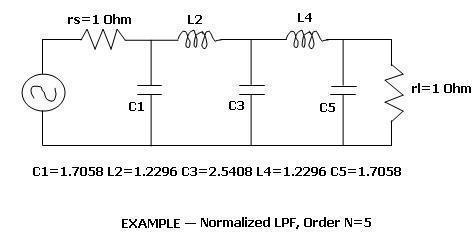
Figure 2: RF Filter Design Example
- Refer RF Filter Design Article for complete step by step guide to design RF filter on microstrip line.
Advertisement
 RF
RF


