Satellite Communication: Types, Architecture, Bands, and Applications
Advertisement
Satellite communication is a critical component of modern communication infrastructure, enabling long-distance data transmission, broadcasting, navigation, and global connectivity. This guide provides an in-depth look at satellite communication, including the fundamentals of satellites, types of satellites including geosynchronous and geostationary, network architecture, frequency bands, orbits, applications and more.
What is a Satellite?
A satellite is an artificial object intentionally placed into orbit around the Earth or another celestial body. Satellites serve various purposes, including communication, weather monitoring, navigation, and scientific research. In satellite communication, these orbiting devices act as relay stations that receive signals from Earth, amplify them, and transmit them back to different locations.
In a C-Band satellite system, a ground station or VSAT transmits at 6 GHz. The satellite receives this 6 GHz signal and translates it to 4 GHz using an on-board LO of frequency 2225 MHz. A hub or Earth station houses an antenna with sizes from 7.5 to 11.2 meters. VSAT houses an antenna of 3.7 or 4.2 meters in size.
A satellite usually will have 12 transponders having 36 MHz bandwidth each. The total bandwidth available is about 500 MHz.
For C band satellites, the uplink frequency is within the 5925 to 6425 MHz range, whereas the downlink frequency is within the 3700 to 4200 MHz range. For Ku band satellites, the uplink is from 14 to 14.5GHz whereas the downlink is from 11.45 to 11.7 GHz range.

Typical specifications of a communication satellite are as follows:
- Frequency band of operation: C band
- Uplink frequency (from ground station to the satellite): 6 GHz
- Downlink frequency (from satellite to the ground station): 4 GHz
- Input Carrier saturation flux density: -85 dBW/meter*meter
- Input carrier backoff: -10dB
- G/T of satellite antenna receive : -5 dB/deg.K
- Single carrier saturated flux density output: 32 dBW
- Output backoff: 4.5 dB
- Uplink path loss : 199.6 dB
- Downlink Path loss: 196.0 dB
- Satellite Intermodulation noise density : -100 dB/Hz
Geosynchronous and Geostationary Satellites
- Geosynchronous Satellite: It is a satellite which has an orbital period matching Earth’s rotation, causing it to return to the same spot in the sky each day.
Examples: Spy satellites, Scientific satellites.
- Geostationary Satellite: A geostationary satellite is a type of geosynchronous satellite that has a circular orbit directly above the Earth’s equator, allowing it to remain fixed over one point on the Earth’s surface. The circular orbit is situated at the altitude of 35768 Kms above the equator of the Earth.
Examples: Communications Satellites, Weather satellites, Navigation Satellites.

Types of Satellites
Satellites are categorized based on their function, orbit, and operational purpose. The main types include following.
- Communication Satellites: Used for telecommunication, broadcasting, internet services, and more. Examples: Intelsat, Eutelsat.
- Weather Satellites: Monitor atmospheric conditions, provide weather forecasts, and track storms. Examples: NOAA, GOES.
- Navigation Satellites: Provide positioning and timing information for GPS and other navigation systems. Examples: GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU).
- Earth Observation Satellites: Used for environmental monitoring, mapping, and disaster management. Examples: Landsat, Copernicus.
- Scientific Satellites: Conduct space and planetary research. Examples: Hubble Space Telescope, James Webb Space Telescope.
- Military Satellites: Used for surveillance, reconnaissance, and secure communications. Examples: Keyhole series, MILSTAR.
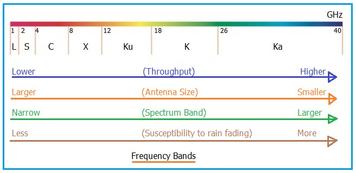
Frequency Bands in Satellite Communication
Satellite communication utilizes specific frequency bands to avoid interference and ensure clear signal transmission. Common frequency bands are mentioned in the following table.
| Band | Frequency Range | Use or application |
|---|---|---|
| L-Band | 1-2 GHz | Used for GPS, mobile satellite phones and marine communication |
| S-Band | 2-4 GHz | Employed in weather satellites and some mobile communications. |
| C-Band | 4-8 GHz | Common in satellite TV broadcasting and data transmission, known for its resistance to rain fade. |
| X-Band | 8-12 GHz | Used primarily for military and government applications. |
| Ku-Band | 12-18 GHz | Widely used for satellite TV, VSAT networks and internet services. |
| K-Band | 18-26.5 GHz | Used for high resolution satellite imagery and some communication services. This band is higher in frequency, which can provide greater data transmission rates but is more susceptible to atmospheric attenuation, such as rain fade. |
| Ka-Band | 26.5-40 GHz | Offers high data rates, suitable for high-speed internet, broadband services, and emerging applications in 5G networks due to its large available bandwidth. The Ka-Band supports high-capacity satellite links, making it ideal for delivering broadband services to consumers, businesses, and mobile platforms. |
Satellite Network Architecture
In a satellite based wireless system, information (voice, data, image, video) is transmitted using microwave radio frequency using a parabolic antenna. Following are the network topologies supported in satellite communication.
- Point-to-Point: Direct communication between two ground stations via a satellite.
- Point-to-Multipoint: A single ground station broadcasts to multiple receivers. As shown in the figure, satellite based internet uses the same topology.
- Mesh Topology: Ground stations communicate directly through a satellite without the need for a central hub.

Satellite communication relies on a network architecture that includes the following key components:
- Space Segment: Comprises the satellite itself, which contains transponders to receive, amplify and retransmit signals.
- Ground Segment: Consists of Earth stations (ground-based antennas) that communicate with the satellites. These stations are responsible for transmitting data to the satellite and receiving data from it.
- User Segment: Includes the end-user devices like satellite phones, TV dishes, and GPS receivers that access satellite services.

There are two modes of satellite based network architecture viz. mesh and star. In mesh mode, VSAT1 and VSAT2 directly communicate using satellite. In star mode, VSAT1 and VSAT2 communicates using Satellite/Hub Station.
Applications of Satellite Communication
Satellite communication plays a vital role in various sectors:
- Telecommunication: Provides backbone connectivity for telephone networks, especially in remote areas.
- Broadcasting: Delivers television and radio services worldwide through direct-to-home (DTH) systems.
- Internet Connectivity: Offers broadband internet access in rural and underserved regions via satellite ISPs.
- Navigation and GPS: Supports global navigation systems that enable precise location tracking and timing.
- Disaster Management: Provides emergency communication and real-time data during natural disasters, aiding rescue and relief operations.
- Military and Defense: Ensures secure, reliable communication for defense operations and intelligence gathering.
- Remote Sensing: Facilitates Earth observation for agriculture, forestry, environmental monitoring, and urban planning.
Advantages of Satellite Communication
The satellite communication advantages or benefits are as follows.
- Global Coverage: Satellites can provide communication services to any location on Earth, including remote and inaccessible areas.
- Scalability: Easily scalable to increase coverage and capacity without significant ground infrastructure.
- Reliability: Less susceptible to natural disasters which usually affects terrestrial networks.
Challenges in Satellite Communication
The satellite communication challenges or limitations are as follows.
- High Initial Costs: Launching and maintaining satellites is expensive.
- Signal Latency: As the signals travel longer distances, geostationary satellites introduce significant amount of delay.
- Interference: Weather conditions like heavy rain can cause signal degradation, especially in higher frequency bands.
Future of Satellite Communication
The future of satellite communication is poised for growth with advancements in technology:
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites: Promises reduced latency and enhanced global broadband coverage (e.g., SpaceX’s Starlink, OneWeb). Due to this, LEO satellites find applications in IoT (Internet of Things) applications.
- 5G Integration: Satellites are expected to play a critical role in complementing 5G networks, especially in remote areas.
- Enhanced Data Rates: New frequency bands and improved satellite technologies will continue to drive higher data rates and connectivity solutions.
Summary
Satellites play a crucial role in the integration of 5G and IoT networks by providing widespread and reliable connectivity, especially in remote and underserved areas where traditional terrestrial networks are impractical. This is achieved through Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations that offer low latency and high speed communication. In the realm of IoT, satellites enable the connection of devices across vast and hard-to-reach locations, by providing ubiquitous and continuous network access.
Advertisement
 RF
RF