Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Tutorial: Protocols, Channels & Technology
Advertisement
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a power-efficient version of the classic Bluetooth standard. It’s designed for applications that need low data rates and very little power. This tutorial will cover the basics of BLE, including the handshake protocols for message exchange, BLE channels, BLE protocol layers, and key differences between BLE and classic Bluetooth. You’ll learn how BLE manages to save energy while still providing reliable communication.
There are many short-range wireless communication applications, like voice, data, audio, and video. Several standards have been developed to support these, including Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, and ANT. Within Bluetooth, different versions cater to varying data rate and distance coverage needs, such as versions 1.2, 2.0, 2.1, 3.0, 4.0, and 4.1. The Bluetooth version 4.0 specification is what we call Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), also known as Bluetooth Smart.
Bluetooth Smart is all about low power, low bandwidth, and low latency data communication. In traditional Bluetooth, a connection is established between devices for communication. Once connected, the link remains active even if there’s no data being transferred. Devices might go to sleep in sniff mode to save battery, but the peak transmit current is still less than 25 mA. While this is less than some other technologies, it’s not low enough for applications powered by coin cell batteries.
BLE is primarily aimed at transferring small chunks of data.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) specifications
| Specification | BLE technology |
|---|---|
| Channel Frequency | 40 channels (3 advertising, 37 data) |
| Distance coverage | 50 meters (150 meters outdoor) |
| Current Consumption | ~15 mA |
| Data rate of operation | 1Mbps |
| Modulation scheme | GFSK |
| Output Power | 10 dBm |
| Device types | Master and Slave |
| Device Modes | Dual mode (Supports BLE and traditional bluetooth), single mode (Support BLE) |
| Wireless Network Modes | Point to Point and Star |
| System Robustness | Adaptive frequency hopping with 24 bit CRC in the packet |
| Security | 128 bit AES CCM |
| Latency | 3 ms |
| Sleep Mode Current | 1 µA |
BLE Network Topology
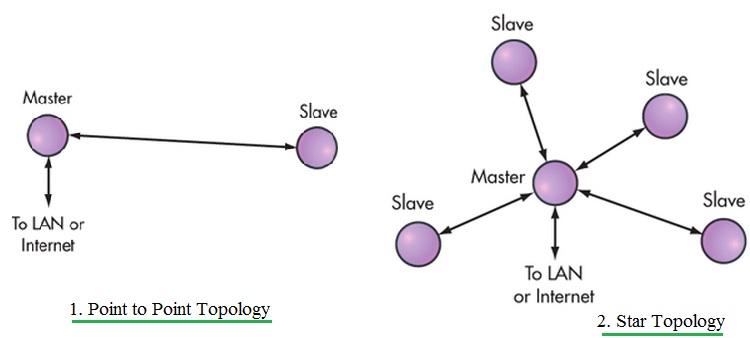
Fig:1 BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) Network
As shown in Figure 1, Bluetooth Low Energy supports both star and point-to-point topologies. Point-to-Point (P2P) is used for pairing two BLE devices, where one acts as the master and the other as the slave. The star topology comes into play when you have multiple BLE nodes. In this setup, one node acts as the central master, while all other nodes function as slaves.
BLE Frequency Channels
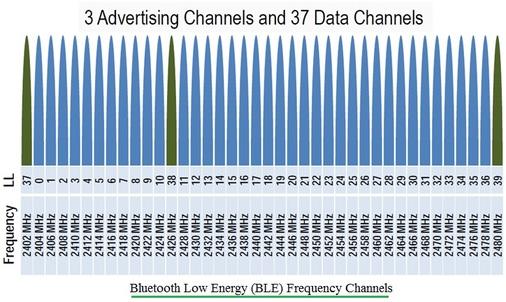
Fig:2 Bluetooth Smart (BLE) Frequency Channels
Figure 2 illustrates the frequency channels used by Bluetooth Smart. It supports 40 channels, each spaced 2 MHz apart. There are 3 advertising channels and 37 data channels. The advertising channels are strategically placed outside the frequency spectrum used by 802.11 to avoid interference.
BLE Message Exchange
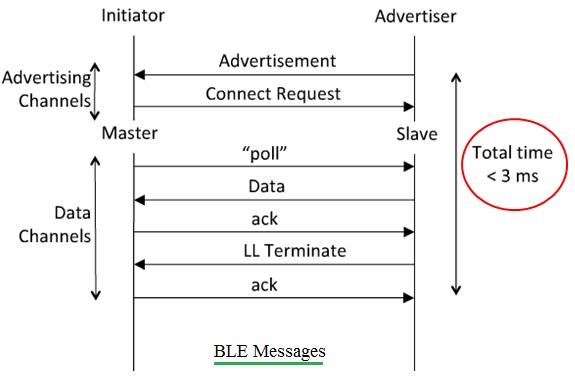
Fig:3 Bluetooth handshake protocol (messages exchanged between BLE devices)
Figure 3 shows the messages exchanged between BLE devices (master and slave).
- Once a connection is established between the master and slave using advertising channels:
- The master informs the slave about the hopping sequence and when to wake up.
- All subsequent transactions use the 37 data channels.
- Encryption can be applied to the data being communicated.
- Both master and slave devices enter a deep sleep mode between transactions.
It takes about 3 ms for a complete data transfer, including the initial message handshake to establish the connection between BLE devices.
Bluetooth Smart (BLE) Protocol Stack
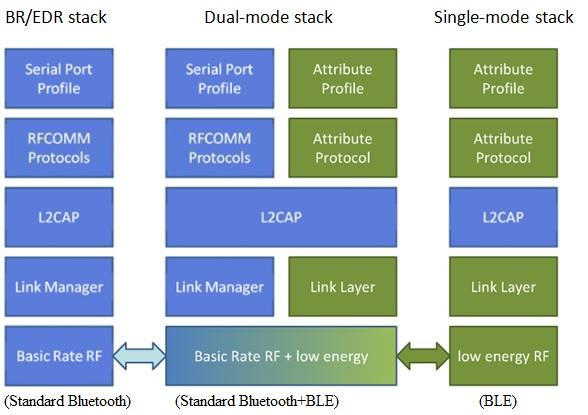
Fig:4 Bluetooth Smart or Bluetooth Low Energy or BLE Stack
Figure 4 depicts the protocol stack for a standard Bluetooth device, a dual-mode device, and a single-mode device. A dual-mode device supports both BLE and standard Bluetooth protocols, allowing it to work with both types of devices.
Bluetooth Smart/Bluetooth Low Energy/BLE Applications (Apps)
Here are some common applications of Bluetooth Smart/Bluetooth Low Energy/BLE technology:
- Proximity
- Time
- Emergency
- Network availability
- Personal User Interface
- Simple remote control
- Browse over Bluetooth
- Generic I/O (automation)
- Temperature Sensor
- Humidity Sensor
- HVAC
- Battery status
- Heart rate monitor
- Physical activity monitor
- Blood glucose monitor
- Cycling sensors
- Pulse Oximeter
- Body thermometer
There are many more BLE apps besides the ones listed here.
Conclusion
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) has changed the game for wireless communication in battery-operated devices. Its low power consumption and reliable performance make it perfect for IoT applications and wearable technologies. Use this guide to implement BLE in your projects, taking advantage of its unique features for power-sensitive applications.
Advertisement
 RF
RF





