Two-Port Network Parameters: Z, Y, h, g, and ABCD
Advertisement
This page delves into the world of two-port network parameters, explaining the ins and outs of impedance (Z) parameters, admittance (Y) parameters, h-parameters, g-parameters, and ABCD parameters.
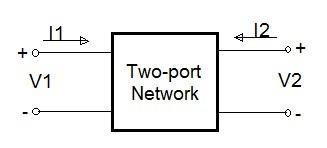
As depicted in the figure above, a two-port network represents a specific instance of a multi-port network, characterized by each port comprising two terminals. Let’s explore each parameter in detail.
Z-Parameters (Open-Circuit Impedance Parameters)
The Z-parameters relate the voltages at the ports to the currents entering them. They are defined by the following equations:
These are also known as open-circuit impedance parameters because each Z-parameter can be found by opening one of the ports (setting its current to zero).
Y-Parameters (Short-Circuit Admittance Parameters)
The Y-parameters, on the other hand, relate the currents at the ports to the voltages applied. They are defined by:
These are called short-circuit admittance parameters because each Y-parameter can be found by shorting one of the ports (setting its voltage to zero).
h-Parameters (Hybrid Parameters)
The h-parameters are a hybrid set, relating the input voltage and output current to the input current and output voltage:
Hybrid parameters are commonly employed in creating models for transistors. They provide a convenient way to characterize the behavior of these devices.
g-Parameters (Inverse Hybrid Parameters)
Similar to h-parameters, g-parameters are another hybrid set, expressing the input current and output voltage in terms of the input voltage and output current:
ABCD-Parameters (Transmission Parameters or T-Parameters)
The ABCD-parameters, also known as transmission parameters, relate the voltage and current at the input port to the voltage and current at the output port:
These parameters are particularly useful for analyzing cascaded networks.
Symmetry and Reciprocity Conditions
The following table summarizes the conditions for a network to be symmetrical and reciprocal, based on its two-port parameters:
| Parameter | Reciprocal | Symmetrical | | --------------- | ------------------ | ----------------- | --- | ---------------------------------- | | Z-parameters | | | | Y-parameters | | | | ABCD-parameters | | | | h-parameters | | | | g-parameters | | |
Advertisement
 RF
RF



