Color Sensors: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advertisement
This page explores the pros and cons of color sensors.
Definition:
A color sensor is a device that detects color. It operates by identifying the wavelengths of different colors. Color sensor-based systems find use in quality control applications, particularly in the textile industry. For example, a wavelength between 450 and 510 nm indicates a blue color, 510 to 560 nm indicates green, and 630 to 780 nm indicates red.
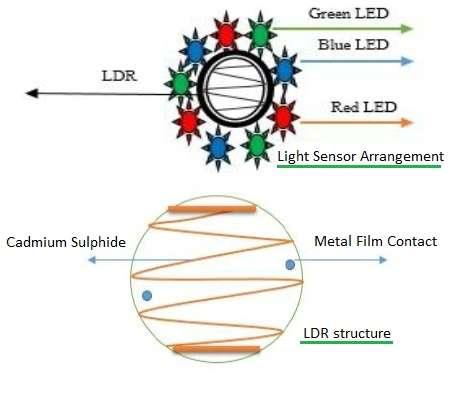
Modern color sensors often incorporate IR filters for more accurate color measurement. They typically include components like Light Dependent Resistors (LDRs) or photodiodes, LEDs, Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs), displays, and microcontrollers in their circuitry.
Color sensors provide two primary types of output: a simple pass/fail condition and a color intensity level. Based on their operational methods, color sensors can be categorized as follows:
- Light to photo-current conversion
- Light to analog voltage converter
- Light to digital conversion
Figure 1 (not provided here) would typically depict an RGB color sensor arrangement.
Several manufacturers produce color sensors, including AMS AG, EMX Industries Inc., and Hamamatsu Photonics.
Advantages of Color Sensors
Here are the benefits of using color sensors:
- Object Sorting and Counting: Color sensors facilitate the sorting of objects based on a three-color approach and can also be used for object counting.
- Automation: Automated systems built with color sensors can complete tasks faster, reducing the need for human intervention.
- Cost-Effective ICs: Powerful color sensor ICs with large memory capacities are available at low cost, driving their use in many applications.
- Easy Setup Modification: Manufacturing setups can be easily changed or modified without needing to reprogram the sensor device, which is beneficial in low-volume manufacturing scenarios with frequent color variations.
- Unlimited Color Matching: With advanced technology and memory loaded with color intensity data, color sensor controllers can store information and make color-matching decisions on virtually unlimited number of colors.
Disadvantages of Color Sensors
Here are the drawbacks of using color sensors:
- Cost for Small Scale Industries: The approach can be too costly for smaller-scale industries.
- Limited Use Cases: It performs color matching or identification in applications requiring only pass/fail output, which might be overkill for some situations.
- Operating Distance: The operating distance range of color sensors can be a concern and requires careful selection and rigorous testing in the setup.
 RF
RF


