WiFi 7 MAC Layer and Frames: AP and Station Architecture
Advertisement
Wi-Fi 7, defined by the IEEE 802.11be standard, introduces significant enhancements to the Medium Access Control (MAC) layer to support Extremely High Throughput (EHT) and optimize performance across various wireless communication scenarios. The MAC layer manages how data is transmitted over the wireless medium, controlling access to the shared radio channels and ensuring efficient communication between devices, including Access Points (APs) and Stations (STAs).
Overview of WiFi 7 MAC Layer Enhancements
The MAC layer in Wi-Fi 7 builds upon the foundation set by Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax). It introduces features to improve throughput, reduce latency, and enhance the overall efficiency of wireless networks.
The key enhancements in the Wi-Fi 7 MAC layer include:
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO): Allows simultaneous use of multiple frequency bands (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz) for data transmission, improving throughput and reliability.
- Enhanced Multi-User (MU) Capabilities: Improvements in MU-OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) and MU-MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) to better handle traffic from multiple users.
- Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN): Introduces mechanisms to support low-latency and time-sensitive applications such as AR/VR and industrial automation.
- Flexible Channel Utilization: Features like preamble puncturing enable more effective use of available spectrum by excluding channels affected by interference.
- Improved Power Save Mechanisms: Enhances power efficiency, particularly for STAs by optimizing sleep and wake cycles through features like Target Wake Time (TWT).
WiFi 7 MAC Architecture
The MAC architecture of WiFi 7 includes several key components that manage data transmission, access coordination, and scheduling.
- MAC Sublayer Management Entity (MLME): Manages MAC operations, including connection establishment, authentication, association, and maintenance of the link.
- MAC Data Service (MAC-D): Handles data transmission and reception, including packet encapsulation, addressing, and fragmentation/reassembly of frames.
- MAC Control Service (MAC-C): Manages the control frames necessary for the coordination of access to the wireless medium such as Request to Send (RTS) and Clear to Send (CTS).
- Channel Access Function: Uses Enhanced Distributed Channel Access (EDCA) to prioritize traffic and manage access contention. Wi-Fi 7 continues to use EDCA with enhancements for better efficiency in dense environments.
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO) Management: Coordinates the use of multiple links (frequency bands) between APs and STAs, which allows aggregated throughput and improved link reliability.

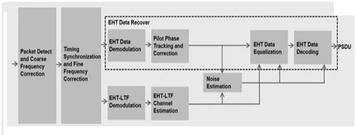
WiFi 7 EHT Frame Structure as per IEEE 802.11be
WiFi 7 MAC Frames for AP and STA
WiFi 7 introduces new frames and extends existing ones to support its advanced features. The common wifi 7 MAC frames are as follows.
-
Beacon Frame: Sent periodically by the AP to announce the presence of the network and provide information about its configuration, including supported MLO capabilities and available channels.
-
Probe Request/Response Frames: Used by STAs to discover available APs in the vicinity and gather information about their capabilities, including MLO support and supported channel widths.
-
Association Request/Response Frames: Sent by STAs to request association with an AP, and responses from the AP confirming the association. These frames include parameters for supported MLO operations and resource allocations.
-
Data Frames: Carry the payload (user data) between APs and STAs. These frames are enhanced to support EHT features such as MLO, higher-order modulation, and improved aggregation techniques.
-
Control Frames:
- RTS/CTS (Request to Send/Clear to Send): Used for coordinating access to the medium and reducing collisions. WiFi 7 maintains these frames with potential extensions for MLO.
- Block Acknowledgement (BA): Supports efficient acknowledgment of multiple data frames, improving throughput by reducing overhead.
-
Management Frames: Includes frames used for network management and configuration, such as Action Frames for negotiating MLO operations, channel switching, and setting up TWT schedules for power-saving.
-
Trigger Frames: Used in MU-OFDMA and MU-MIMO operations to trigger STAs to transmit data in allocated RUs. Wi-Fi 7 enhances these frames for more efficient multi-user communication.
Wi-Fi 7 MAC Layer Operation for AP and STA
Access Point (AP) Role
- Central Coordination: The AP coordinates MLO operations, schedules resources for MU-OFDMA and MU-MIMO, and manages TSN to ensure low-latency communication.
- Frame Aggregation: APs use frame aggregation techniques like A-MPDU (Aggregated MAC Protocol Data Unit) and A-MSDU (Aggregated MAC Service Data Unit) to improve throughput.
- Channel Access Management: The AP uses EDCA and enhancements to manage channel access, balancing contention and ensuring QoS for various types of traffic.
Station (STA) Role
- Resource Utilization: STAs participate in MLO by connecting to APs over multiple links, optimizing data transmission across different bands.
- Power Management: STAs leverage TWT and other power-saving features to minimize energy consumption while maintaining connectivity.
- Adaptive Response: STAs adjust their behavior based on AP signals, such as responding to trigger frames for efficient uplink transmissions.
Summary
The WiFi 7 MAC layer enhancements are crucial for supporting extremely high throughput, reduced latency, and improved efficiency.
Advertisement
 RF
RF